最近把《程序员的自我修养–链接、装载与库 》这本书又重新温习了下,加深了对可执行文件的理解,这篇文章就结合 fishhook 来实践一下。
Demo - NSLog 先从一个 NSLog 的 Demo 实践开始,讲解调用系统库函数 NSLog 的执行流程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { NSString * appDelegateClassName; @autoreleasepool { // Setup code that might create autoreleased objects goes here. appDelegateClassName = NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class]); NSLog(@"%@", @"hello world"); } return UIApplicationMain(argc, argv, nil, appDelegateClassName); }
lldb 在 NSLog 处下断点,并在 Xcode 设置 debug -> debug workflow -> always show disassembly 查看其汇编实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 0x10fcf0a79 <+89>: leaq 0x26f20(%rip), %rdi ; @"%@" 0x10fcf0a80 <+96>: leaq 0x26f39(%rip), %rsi ; @"hello world" -> 0x10fcf0a87 <+103>: movb $0x0, %al 0x10fcf0a89 <+105>: callq 0x10fd12000 ; symbol stub for: NSLog 0x10fcf0a8e <+110>: movq -0x20(%rbp), %rdi 0x10fcf0a92 <+114>: callq 0x10fd122ac ; symbol stub for: objc_autoreleasePoolPop
在 0x10fd12000 处下断点
1 2 (lldb) b 0x10fd12000 Breakpoint 3: where = Demo_fishhook`symbol stub for: NSLog, address = 0x000000010fd12000
单步执行过掉 NSLog 处的断点,到
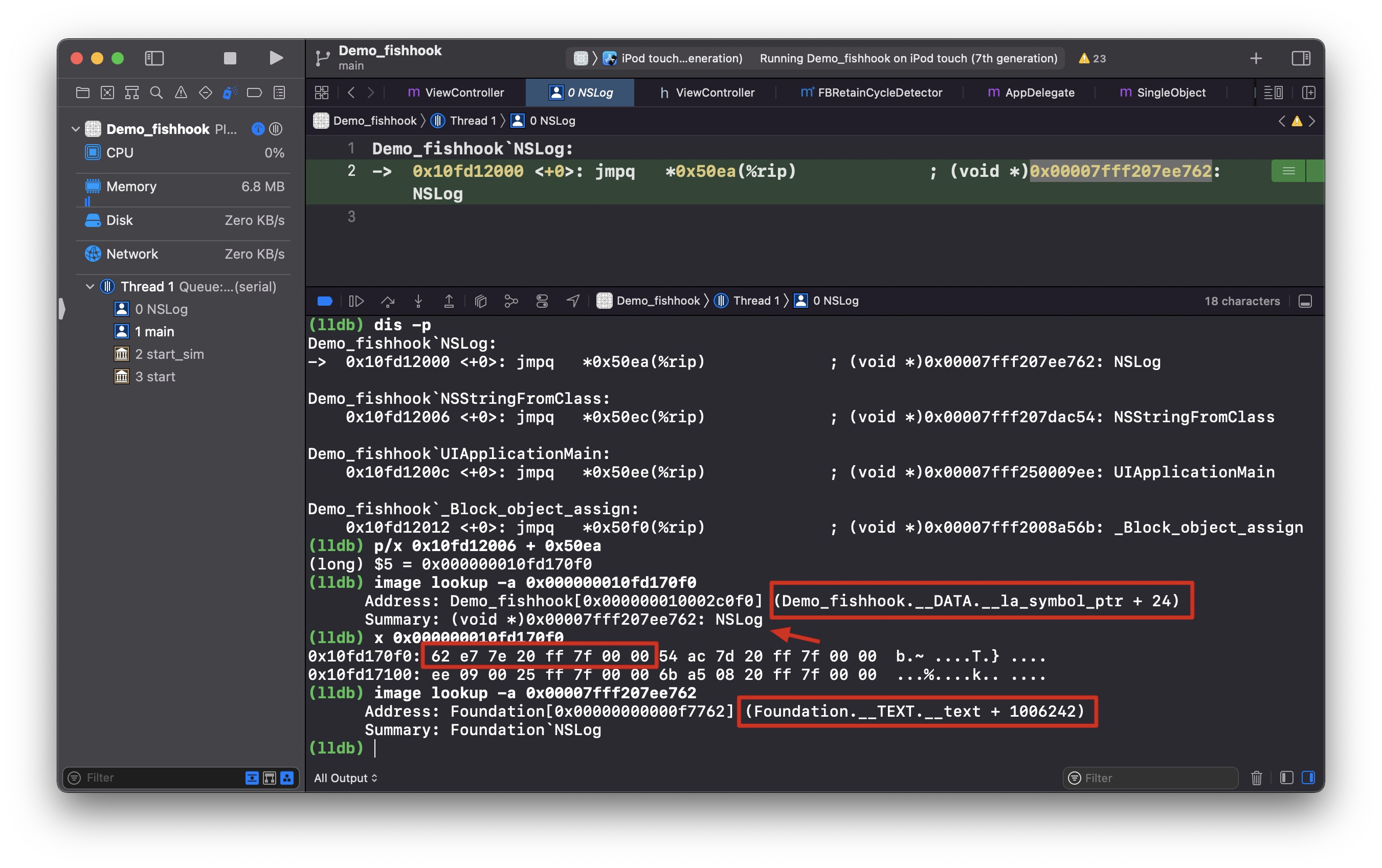
1 2 Demo_fishhook`NSLog: -> 0x10fd12000 <+0>: jmpq *0x50ea(%rip) ; (void *)0x00007fff207ee762: NSLog
这条指令的意思获取 rip + 0x50ea 地址(A),然后跳转到该地址存储的值(B)(类比二级指针)。
那我们先找出 rip 的地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 (lldb) register read General Purpose Registers: rax = 0x0000600002f3e400 rbx = 0x000000010fda3060 rcx = 0x0000000114fbf600 dyld`_main_thread rdx = 0x000000000000002c rdi = 0x000000010fd179a0 @"%@" rsi = 0x000000010fd179c0 @"hello world" rbp = 0x00007ff7b0212ca0 rsp = 0x00007ff7b0212c78 r8 = 0x00007fff862a40c0 libsystem_pthread.dylib`_pthread_keys r9 = 0x0000000000000000 r10 = 0x00007fff862da642 (void *)0xe6b800007fff862d r11 = 0x00007fff2019c15c libobjc.A.dylib`-[NSObject autorelease] r12 = 0x0000000114fbf3a0 dyld`_NSConcreteStackBlock r13 = 0x00007ff7b0212d68 r14 = 0x000000010ff98e14 dyld_sim`start_sim r15 = 0x0000000114fb3010 dyld`dyld4::sConfigBuffer rip = 0x000000010fd12000 Demo_fishhook`symbol stub for: NSLog rflags = 0x0000000000000246 cs = 0x000000000000002b fs = 0x0000000000000000 gs = 0x0000000000000000
当前指令还卡在 0x000000010fd12000 处,所以 rip 还是它。那怎么知道 0x000000010fd12000 下一条指令的地址呢?也就是 0x000000010fd12000 这条指令的长度(PS: 按道理应该有文档能找到 AT&T X86-64 汇编 jmpq 指令的长度,但没搜到)。lldb dis 乱猜一通,于是就有了下面的结果。
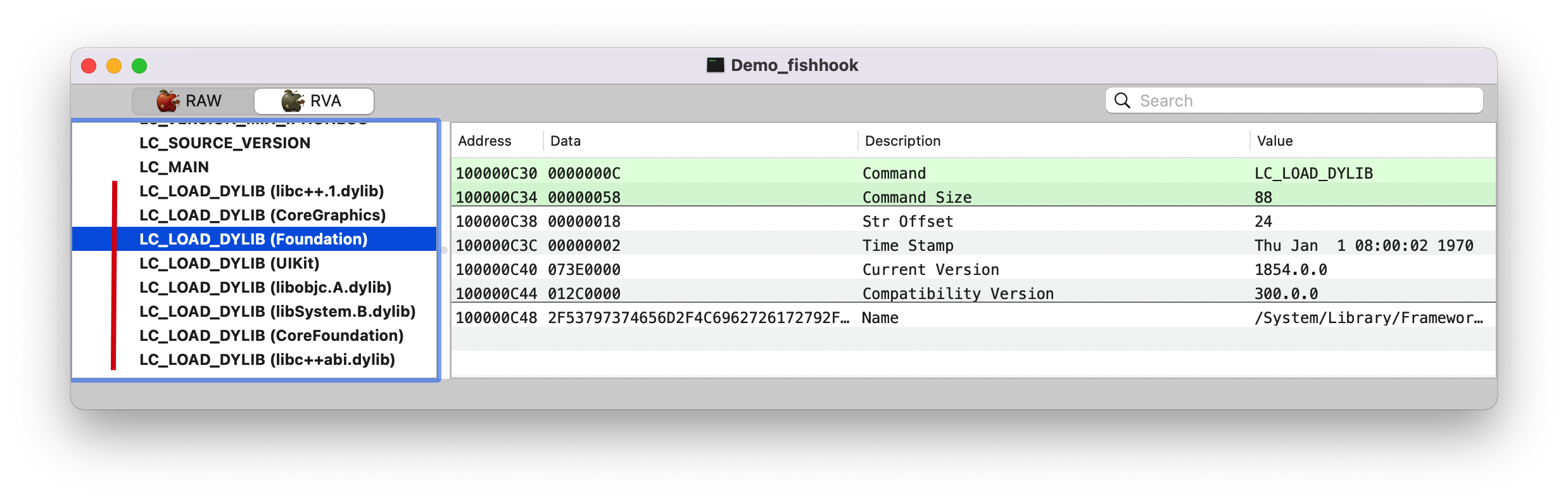
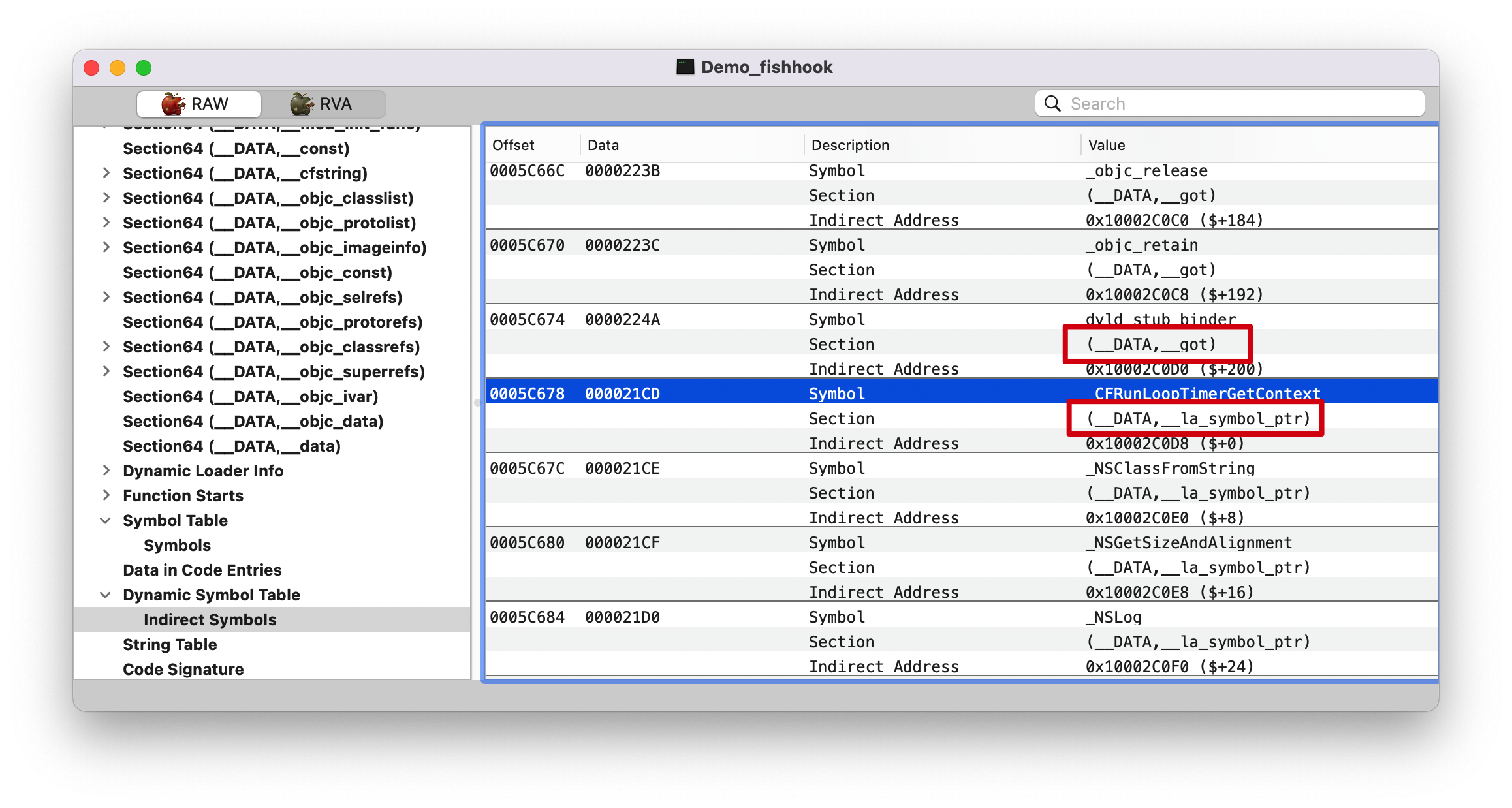
0x10fd12000 下一条指令是 0x10fd12006,所以地址(A)就是 0x000000010fd170f0,而 0x000000010fd170f0 里面存储的值(B)就是 0x00007fff207ee762,在系统库 Foundation 里面,也就是找到 NSLog 的实现了。这跟 fishhook 源码解析 里面提到的第一次会通过 __stub_helper 去查找不符合,这里 __DATA,__la_symbol_ptr 直接存储的就是实际地址值了。(PS: 我 Xcode 版本是 Version 13.1 (13A1030d),通过下断点得知是 dyld4, 我以为是 dyld4 做了什么优化,把电脑重启后再次运行还是一样的结果。)
Note :
大小端,内存地址存储的值是小端模式,即 0x10fd170f0: 62 e7 7e 20 ff 7f 00 00
lldb image 指令的其他玩法,可以在 help 调试下输入 image help 查看
MachOView 既然 lldb 调试推理不出 __stub_helper,那就看下是否能通过 macho 可执行文件里面存储的原始值能推理出来不?
还是前面的断点
1 2 3 (lldb) image lookup -a 0x10fd12000 Address: Demo_fishhook[0x0000000100027000] (Demo_fishhook.__TEXT.__stubs + 18) Summary: Demo_fishhook`symbol stub for: NSLog
在 __TEXT.__stubs section, 用 MachOView 来查看该 Demo 的可执行文件。
Note :
0x10fd12000 是虚拟内存地址0x0000000100027000 是加上虚拟基地址的文件偏移(offset), 而虚拟基地址一般都是 0x0000000100000000, 即 2^32.
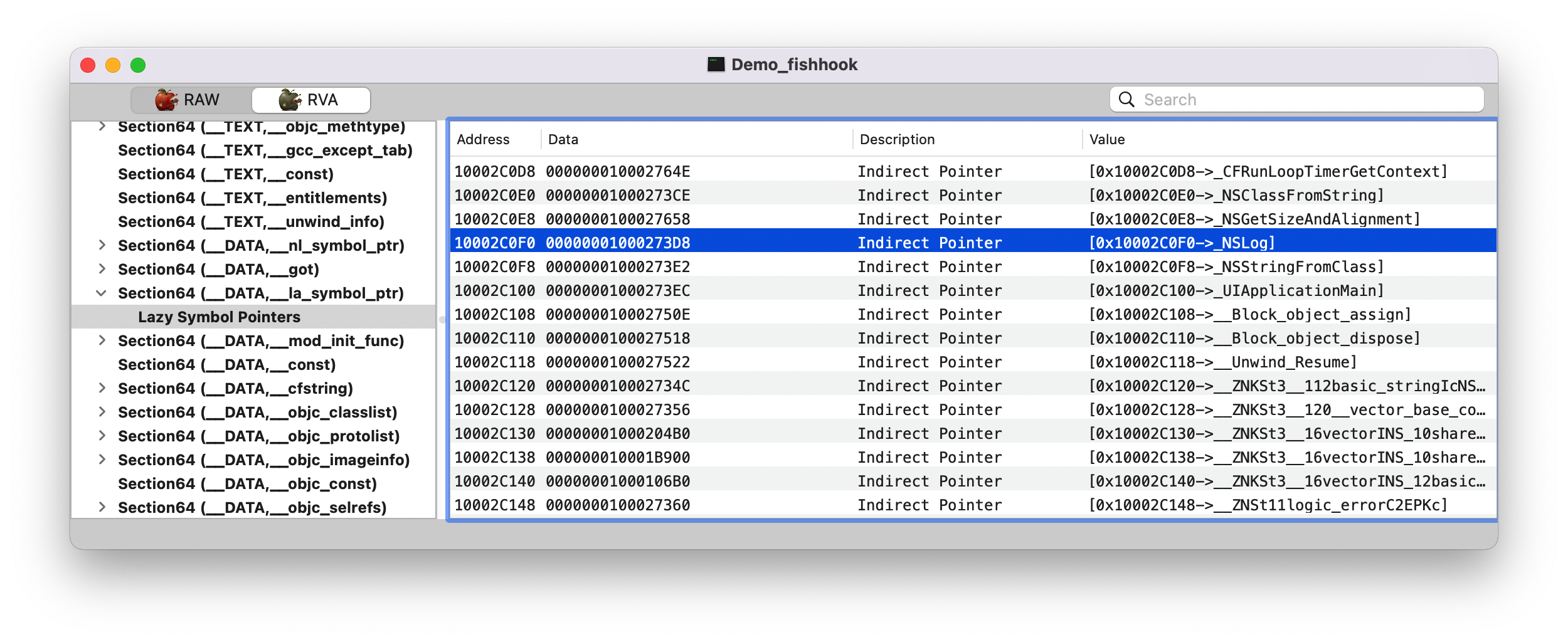
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 (lldb) image list // 得出该可执行文件 image 在虚拟内存中的起始地址:`0x000000010fceb000` [ 0] 0D70A5F7-C54D-312D-B242-ADE1AB9BEF9D 0x000000010fceb000 /Users/joakim/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Demo_fishhook-ebwkhxbcogafxbclcdeifrppsgdu/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/Demo_fishhook.app/Demo_fishhook /Users/joakim/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Demo_fishhook-ebwkhxbcogafxbclcdeifrppsgdu/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/Demo_fishhook.app.dSYM/Contents/Resources/DWARF/Demo_fishhook (lldb) image list -o -f // 得到可执行文件的 ASLR 值 [ 0] 0x000000000fceb000 /Users/joakim/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Demo_fishhook-ebwkhxbcogafxbclcdeifrppsgdu/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/Demo_fishhook.app/Demo_fishhook (lldb) p/x 0x000000010fceb000 - 0x000000000fceb000 (long) $0 = 0x0000000100000000 // 上面两个地址相减,就得到了虚拟基址 (lldb) p/x 0x0000000100027000 - 0x0000000100000000 // 得到 `Demo_fishhook.__TEXT.__stubs` 在 macho 文件中的 offset (long) $1 = 0x0000000000027000 (lldb) p/x 0x10fd12006 + 0x50ea - 0x000000000fceb000 // 得到前面提到的地址 A, 还是通过前面 lldb 计算得来,发现跟下面 MachOView 所查看到的是一样的 (int) $2 = 0x000000010002c0f0
在 RVA tab 找到 0x000000010002c0f0 地址Data 那一栏的值 00000001000273D8, 继续查找。
RVA: Relative Virtual Address, 相对虚拟地址(没添加 ASLR 的值)
RAW: offset, 在 macho 文件中的偏移
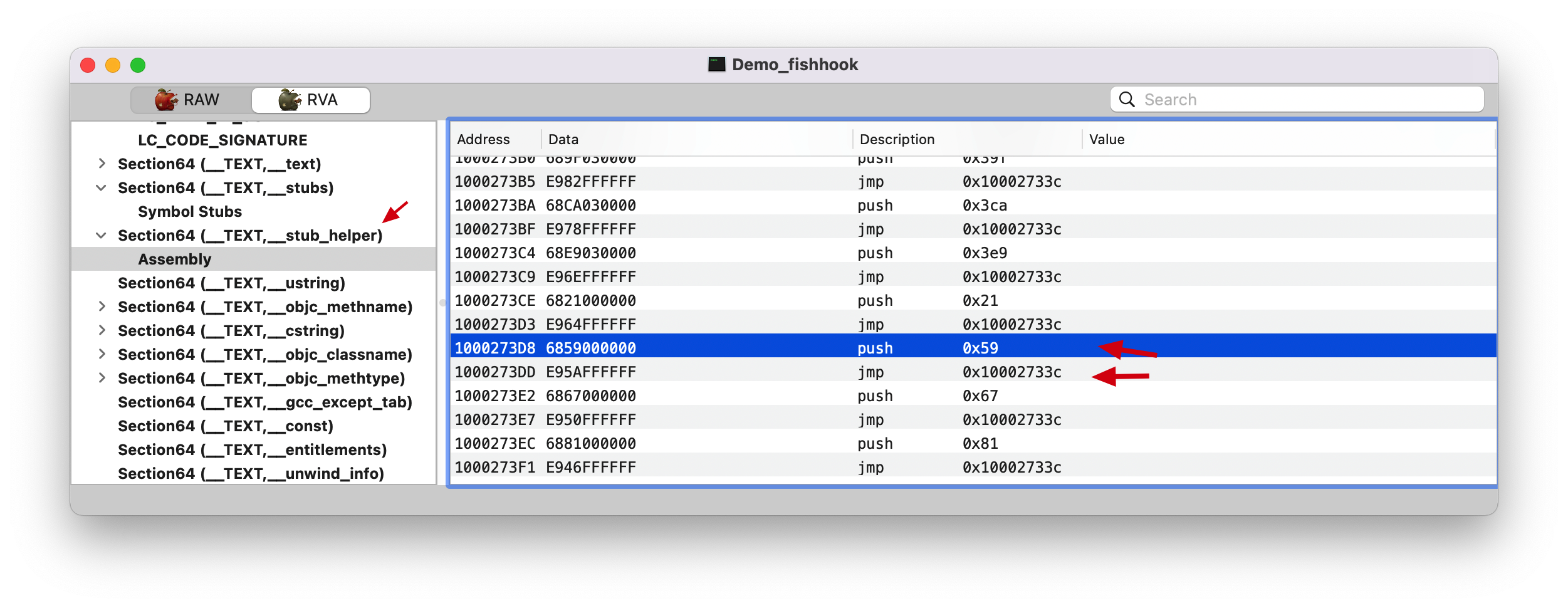
push 0x59 push 0x59: 表示将 0x59 立即数入栈,而我们知道栈一般用做函数调用时的传参。AntiHook 的内容可知
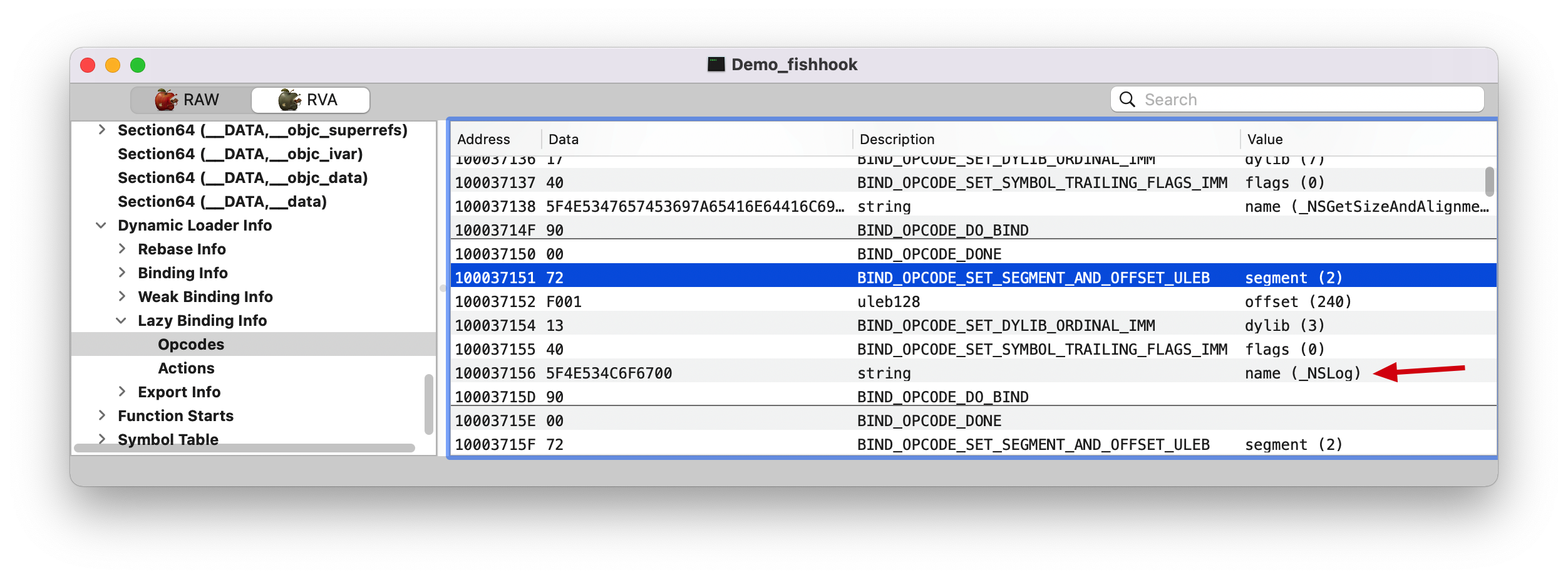
其实在dyld源码里,dyld_ stub_bind最后会调用fastBindLazySymbol函数,这个函数的第二个参数是lazyBindingInfoOffset, 即0x0120是Binding Info或者Lazy Binding Info区起始开始到符号信息的偏移,而符号信息如下图
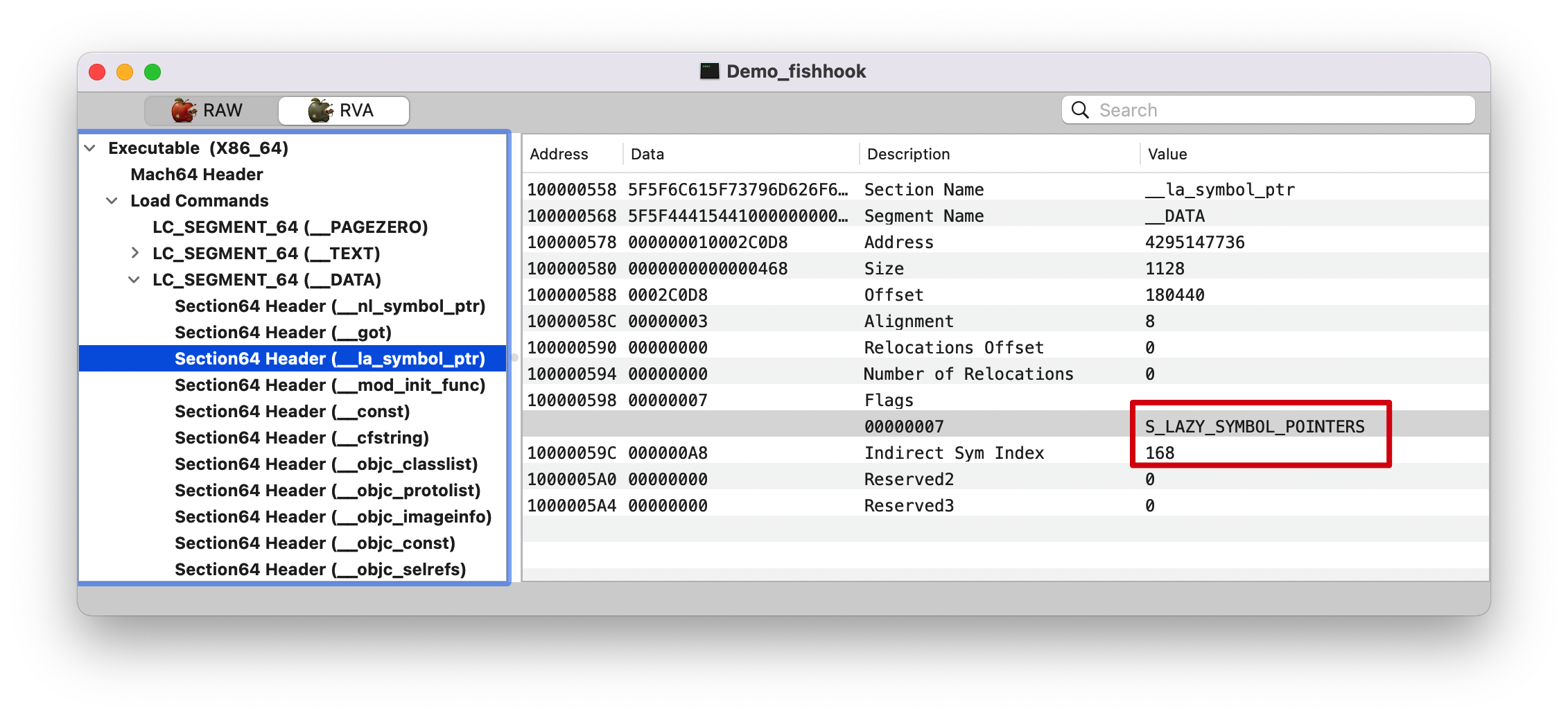
因为 NSLog 符号在 __DATA,__la_symbol_ptr(la: lazy), 所以就是相对于 Lazy Binding Info 偏移 0x59 。
1 2 (lldb) p/x 0x1000370F8 + 0x59 (long) $17 = 0x0000000100037151
name(_NSLog)。dylib(3) 呢?表示该符号在所加载的第3个 dylib 里面(如下图)。Note: 从这里可以看出,进行链接的时候会把动态库里符号的相关信息存储起来(即:该符号属于哪个动态库)。
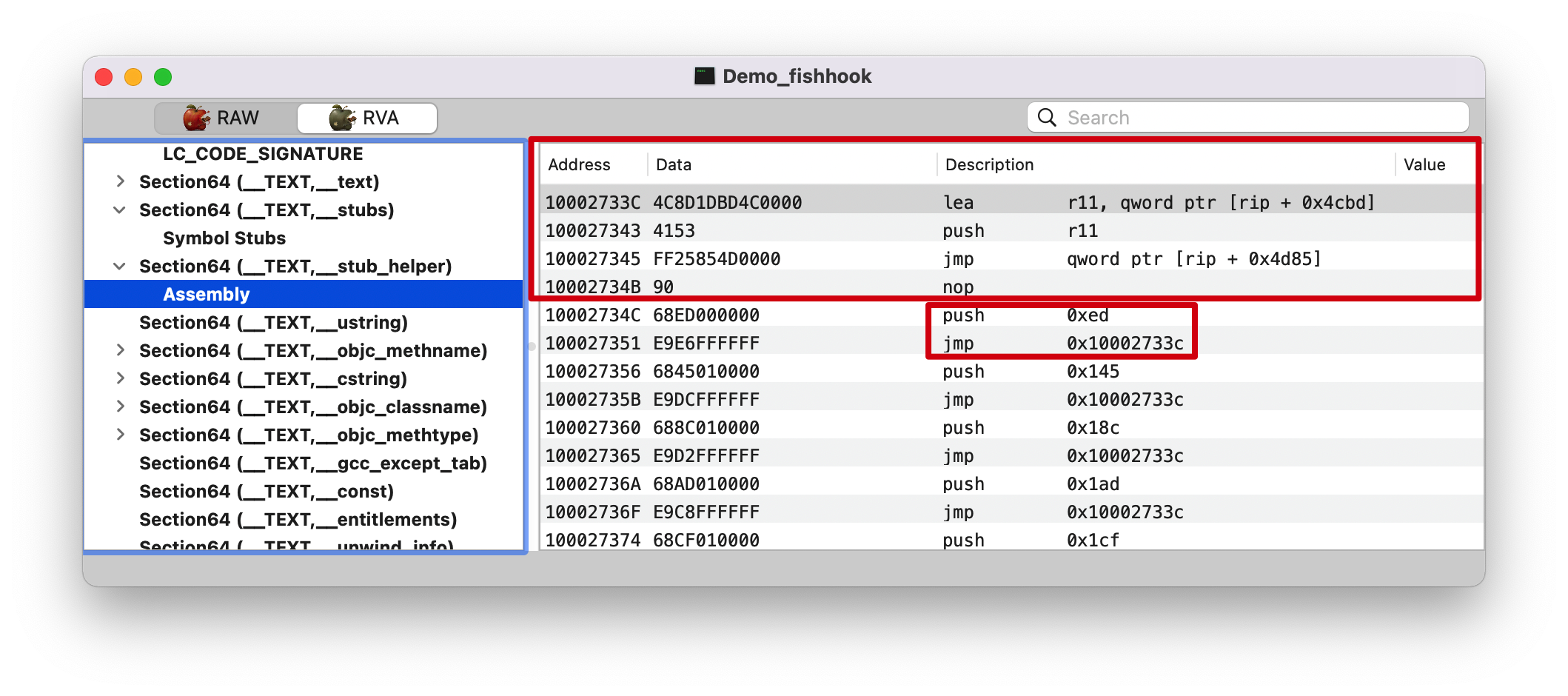
jmp 0x10002733c
lea r11, qword ptr [rip + 0x4cbd]
将 rip + 0x4cbd = 0x100027343 + 0x4cbd = 0x000000010002c000 地址的值存入 r11 寄存器
push r11
所以此时栈中有两个参数:前面的 0x59; 这里的 0x000000010002c000
jmp qword ptr [rip + 0x4d85]
跳转到 rip + 0x4cbd = 0x10002734B + 0x4d85 = 0x000000010002c0d0 执行函数
注意:这里分为两块
前面这一块的就是 __stub_helper 的具体执行逻辑
后面这一块就是传参、然后调用 __stub_helper // 而这里的参数具体在前面讲解 0x59 的时候有提到
1 2 3 4 5 (lldb) p/x 0x000000000fceb000 + 0x10002C000 (long) $24 = 0x000000010fd17000 (lldb) x 0x000000010fd17000 0x10fd17000: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 94 4d 8a ff 7f 00 00 ..........M..... 0x10fd17010: 08 28 2a 86 ff 7f 00 00 1a 33 25 20 ff 7f 00 00 .(*......3% ....
诶,在程序启动后,它的值还是为 0, 这是为什么呢?
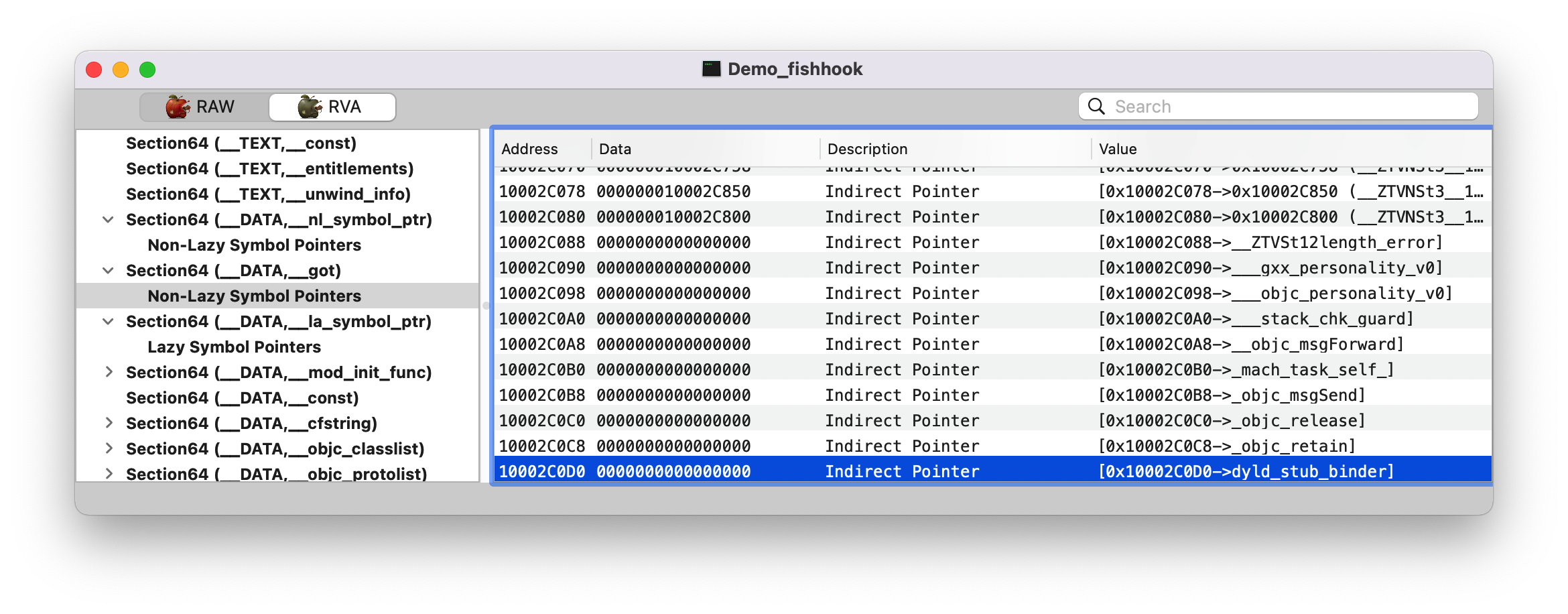
dyld_stub_binder 了,并且它已经有值了。
1 2 3 4 5 (lldb) p/x 0x000000000fceb000 + 0x10002C0D0 (long) $25 = 0x000000010fd170d0 (lldb) x 0x000000010fd170d0 0x10fd170d0: 80 a6 2c 86 ff 7f 00 00 b9 85 36 20 ff 7f 00 00 ..,.......6 .... 0x10fd170e0: 10 ad 7d 20 ff 7f 00 00 84 c0 3f 20 ff 7f 00 00 ..} ......? ....
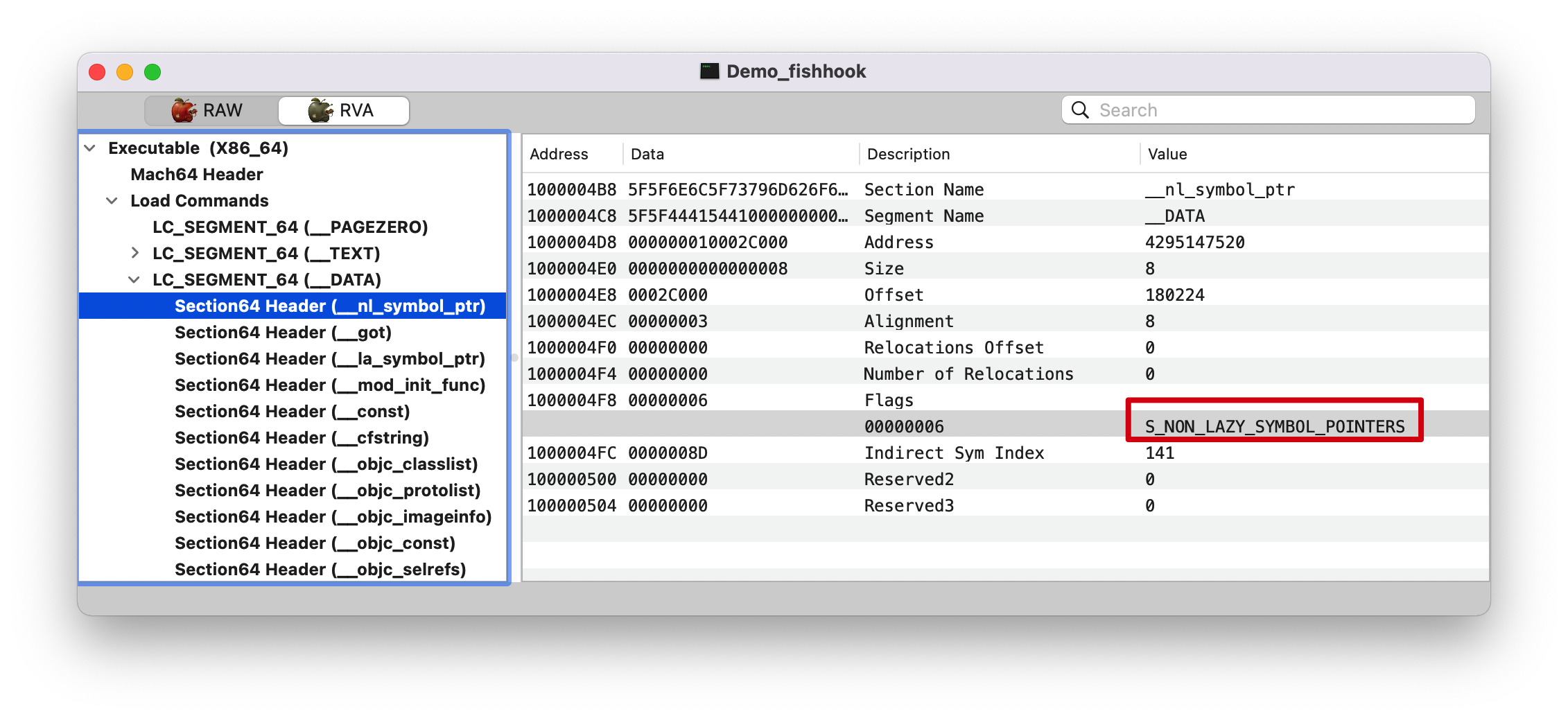
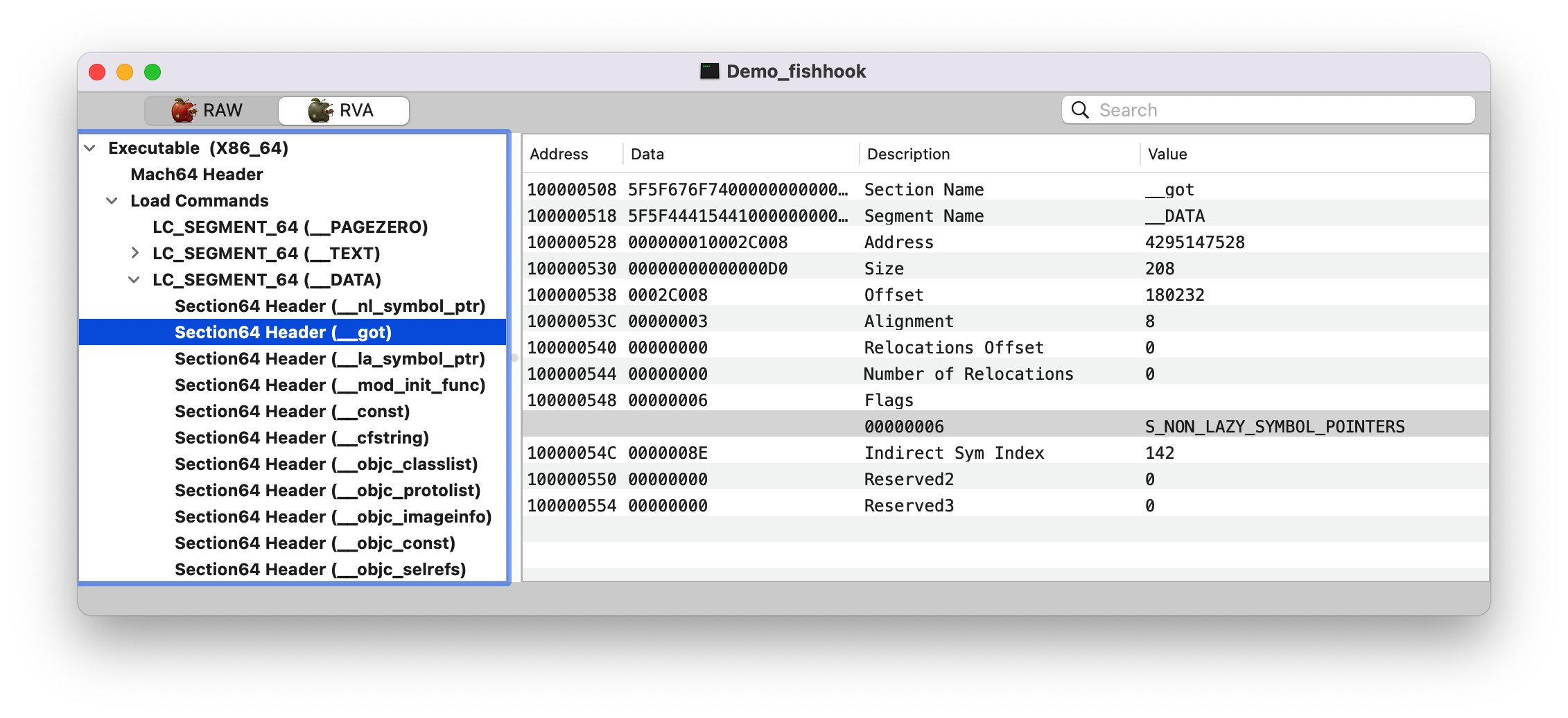
Note :这里的 __DATA,__nl_symbol_ptr 和 __DATA,__got Section 都是属于非懒加载的,在程序启动时 dyld 就会修正这些符号值。
Note : 注意这里的 Indirect Sym Index(Reserved1): 168, 后面讲解 fishhook 的时候会提到。
因为它们存在于有可读可写权限的 DATA Segment。
总结 NSLog 这块的逻辑大致分为
lazy binding 的符号地址最开始指向 __TEXT,__stubs 里所指向的方法,调用该方法的时候,它会调用 __DATA,__la_symbol_ptr 所指向地址里面的方法
未绑定的时候,__DATA,__la_symbol_ptr 指向 ___TEXT,__stub_helper ,而后者会执行系统函数(dyld_stub_binder)找到方法实现后,会修改 __DATA,__la_symbol_ptr 的值,从而指向实际的函数地址
已绑定的时候,__DATA,__la_symbol_ptr 则指向实际的函数地址。// 而 fishhook 就是这么干的,修改 __DATA,__la_symbol_ptr 里面相关符号的值
fishhook 有了前面 NSLog lazy binding 的调试经验,现在调试 fishhook 就会轻松很多。这里的 Demo 参考自 fishhook 源码解析 。
rebind_symbols 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 struct rebindings_entry { struct rebinding *rebindings; // rebinding 类型的数组 size_t rebindings_nel; // 该数组的长度 struct rebindings_entry *next; // 链表的下一个 entry }; // 链表头 static struct rebindings_entry *_rebindings_head; int rebind_symbols(struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t rebindings_nel) { // 维护一个 rebindings_entry 的结构 // 将 rebinding 的多个实例组织成一个链表 int retval = prepend_rebindings(&_rebindings_head, rebindings, rebindings_nel); // 判断是否 malloc 失败,失败会返回 -1 if (retval < 0) { return retval; } // _rebindings_head -> next 是第一次调用的标志符,NULL 则代表第一次调用 if (!_rebindings_head->next) { // 第一次调用,将 _rebind_symbols_for_image 注册为回调 _dyld_register_func_for_add_image(_rebind_symbols_for_image); } else { // 先获取 dyld 镜像数量 uint32_t c = _dyld_image_count(); for (uint32_t i = 0; i < c; i++) { // 根据下标依次进行重绑定过程 _rebind_symbols_for_image(_dyld_get_image_header(i), _dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(i)); } } // 返回状态值 return retval; }
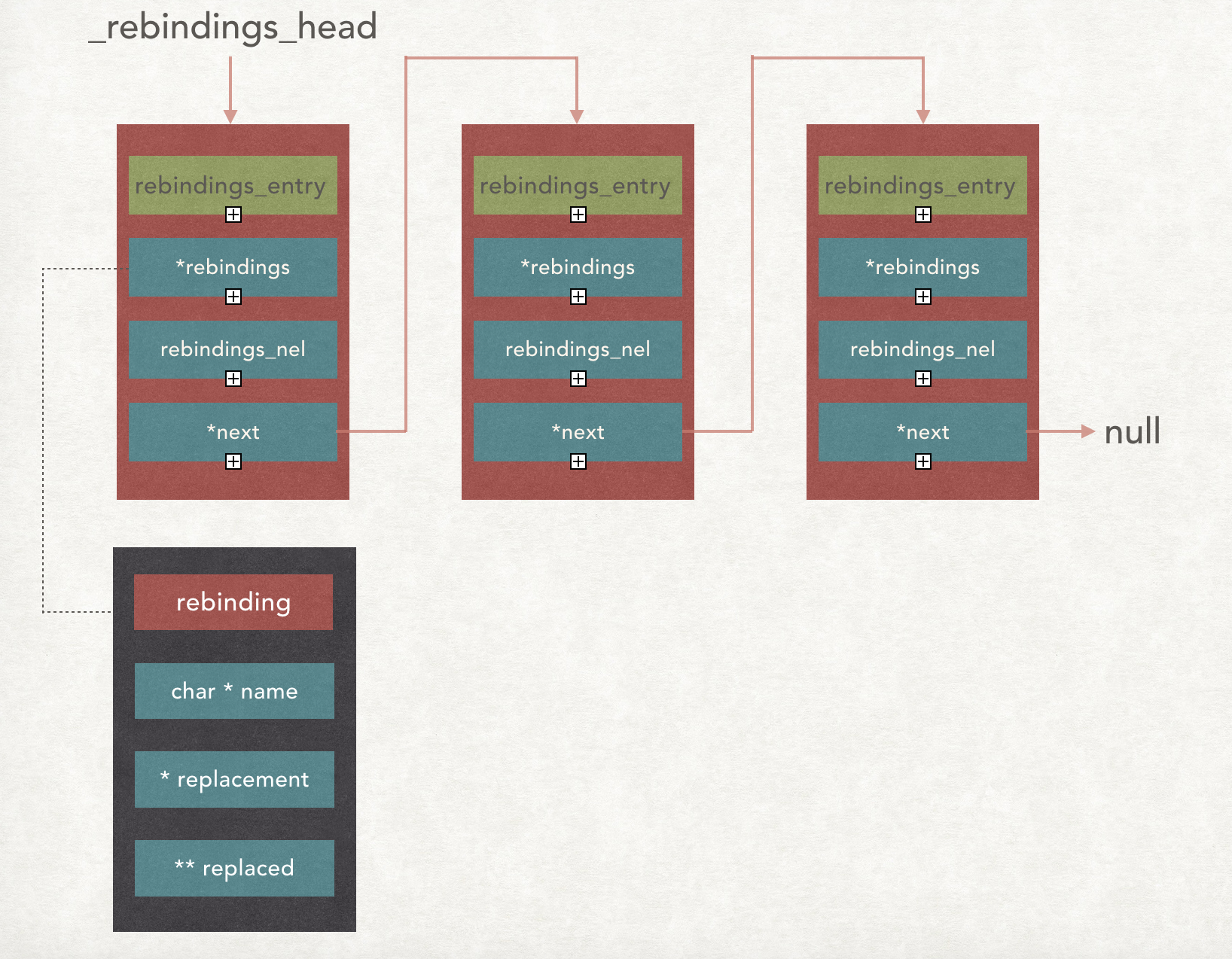
prepend_rebindings 该方法使用链表存储 rebindings_entry 结构,使用头插法将一个链表串起来,链表头用 _rebindings_head 保存。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static struct rebindings_entry *_rebindings_head; /* rebindings_head: 静态的链表头 rebindings: 方法符号数组 nel: 数组长度 */ static int prepend_rebindings(struct rebindings_entry **rebindings_head, struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t nel) { // 声明 rebindings_entry 一个指针,并为其分配空间 struct rebindings_entry *new_entry = (struct rebindings_entry *) malloc(sizeof(struct rebindings_entry)); if (!new_entry) { return -1; } // 为数组 rebindings 分配内存 new_entry->rebindings = (struct rebinding *) malloc(sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel); if (!new_entry->rebindings) { free(new_entry); return -1; } // 内存拷贝,将 rebindings 数组中 copy 到 new_entry -> rebingdings 成员中 memcpy(new_entry->rebindings, rebindings, sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel); new_entry->rebindings_nel = nel; // 头插法 new_entry->next = *rebindings_head; *rebindings_head = new_entry; return 0; }
经过多次操作后,结果如下图所示
Note : 这里 *rebindings 是一个数组。
_rebind_symbols_for_image _dyld_register_func_for_add_image 方法是 dyld 注册回调函数的方法,当镜像被加载的时候,就会主动触发注册的回调方法。
一个可执行文件会加载非常多的动态库,每个动态库的成功加载都会触发注册的回调方法。每个动态库镜像都会根据设置重绑定符号
这里多个 image 可以在程序运行的时候通过 image list 获取。
而这里,就注册了 _rebind_symbols_for_image 方法,但里面没做任何事情,直接调用另外一个方法。
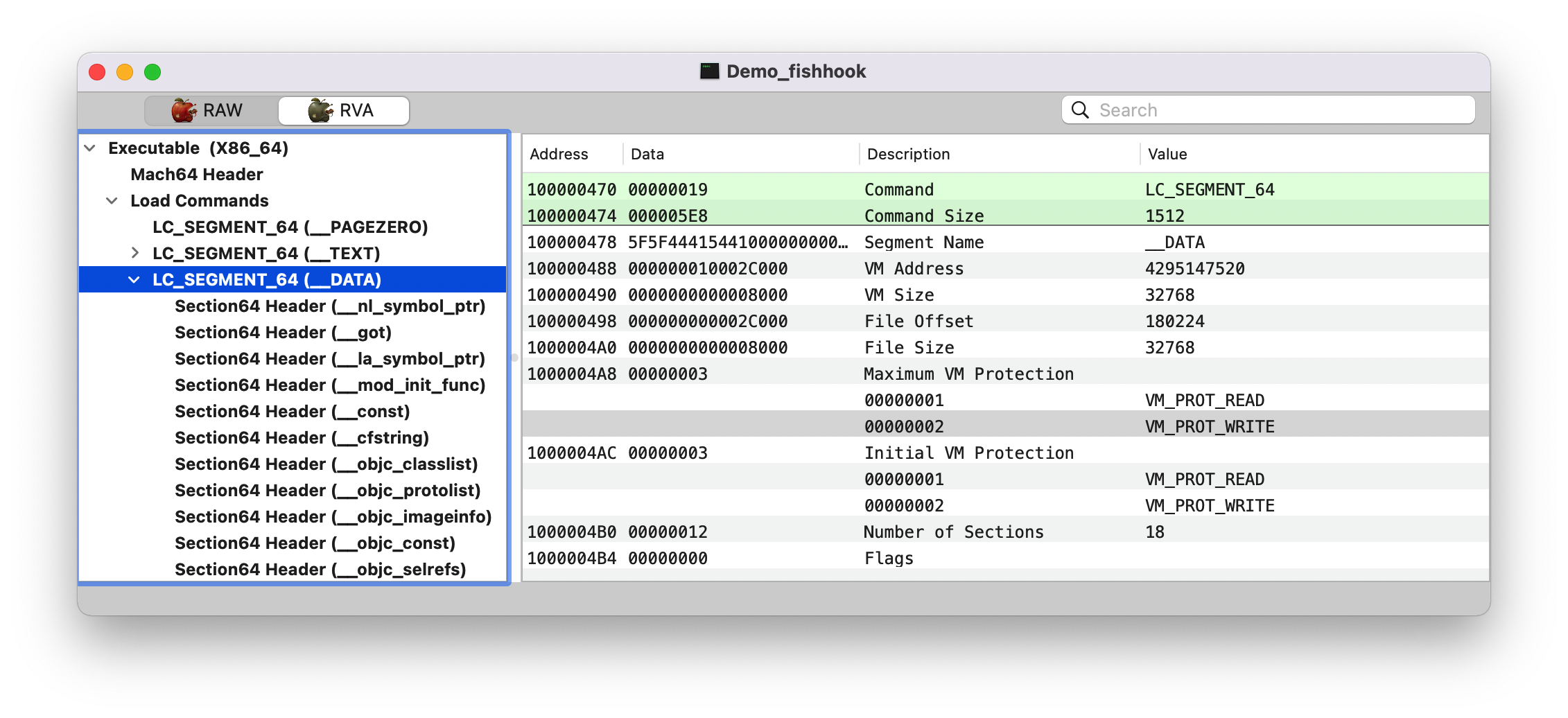
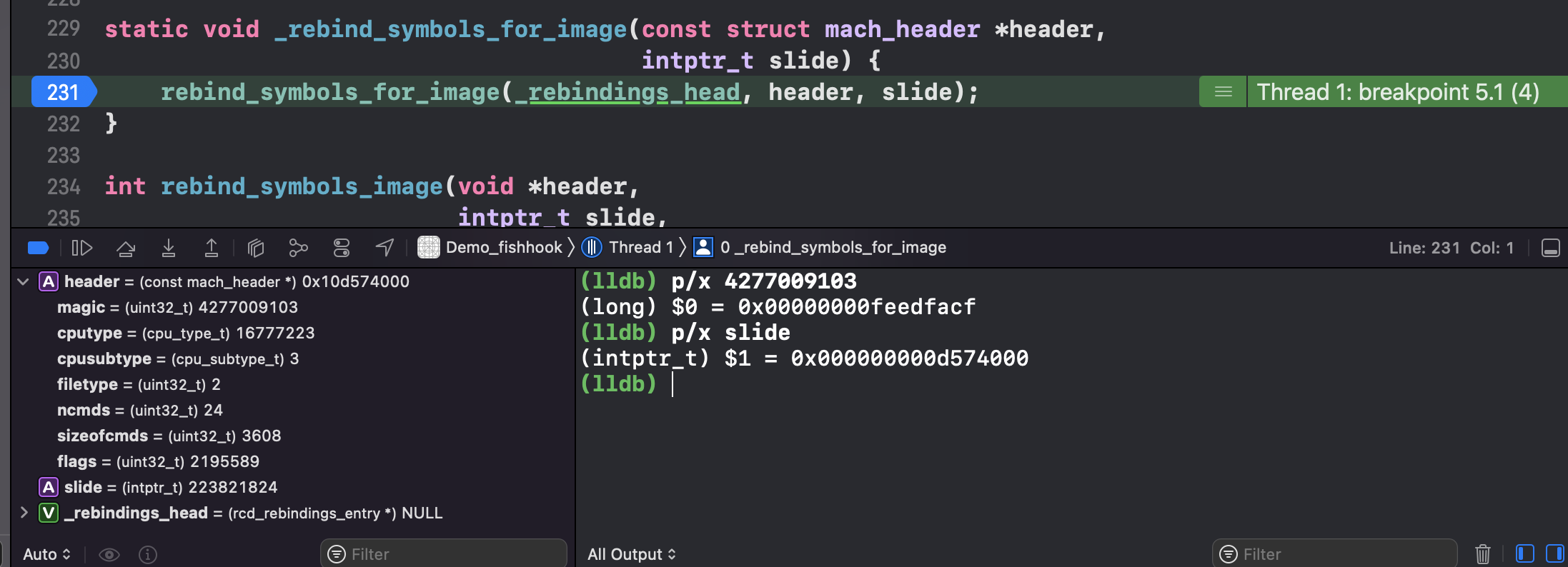
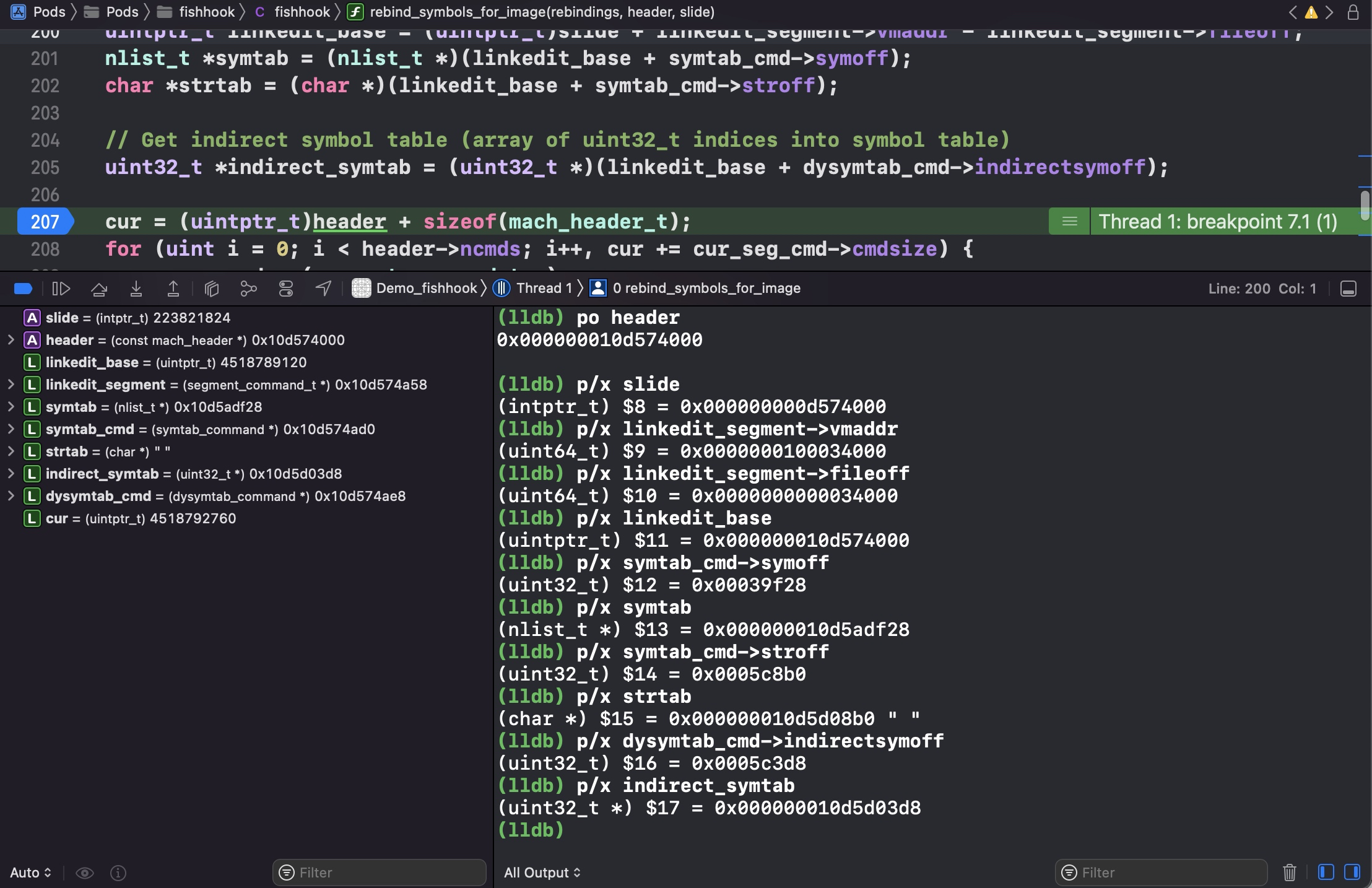
header: 当前可执行文件的虚拟内存地址;也就是 image 的 header 头信息,结构体如下图所示1 2 3 (lldb) image list [ 0] 0D70A5F7-C54D-312D-B242-ADE1AB9BEF9D 0x000000010d574000 /Users/joakim/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Demo_fishhook-ebwkhxbcogafxbclcdeifrppsgdu/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/Demo_fishhook.app/Demo_fishhook /Users/joakim/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Demo_fishhook-ebwkhxbcogafxbclcdeifrppsgdu/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/Demo_fishhook.app.dSYM/Contents/Resources/DWARF/Demo_fishhook
slide: ASLR 偏移值1 2 (lldb) image list -o -f [ 0] 0x000000000d574000 /Users/joakim/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Demo_fishhook-ebwkhxbcogafxbclcdeifrppsgdu/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/Demo_fishhook.app/Demo_fishhook
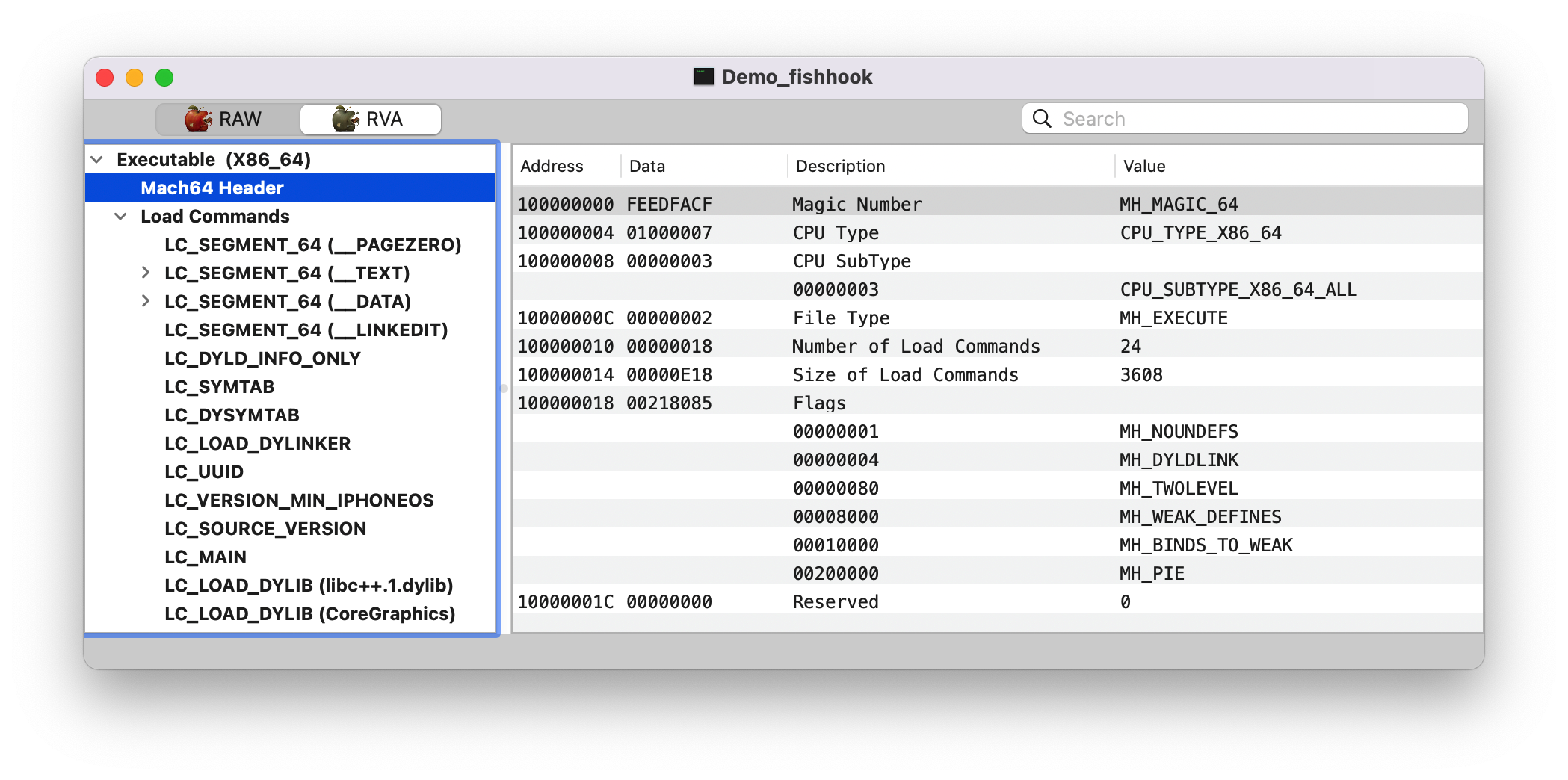
magic: 0x00000000feedfacf, 同 MachOView 那一栏的值,这里是大端模式1 2 (lldb) p/x 4277009103 (long) $2 = 0x00000000feedfacf
Note: 该进程有多少个 image, 该方法就会回调多少次。
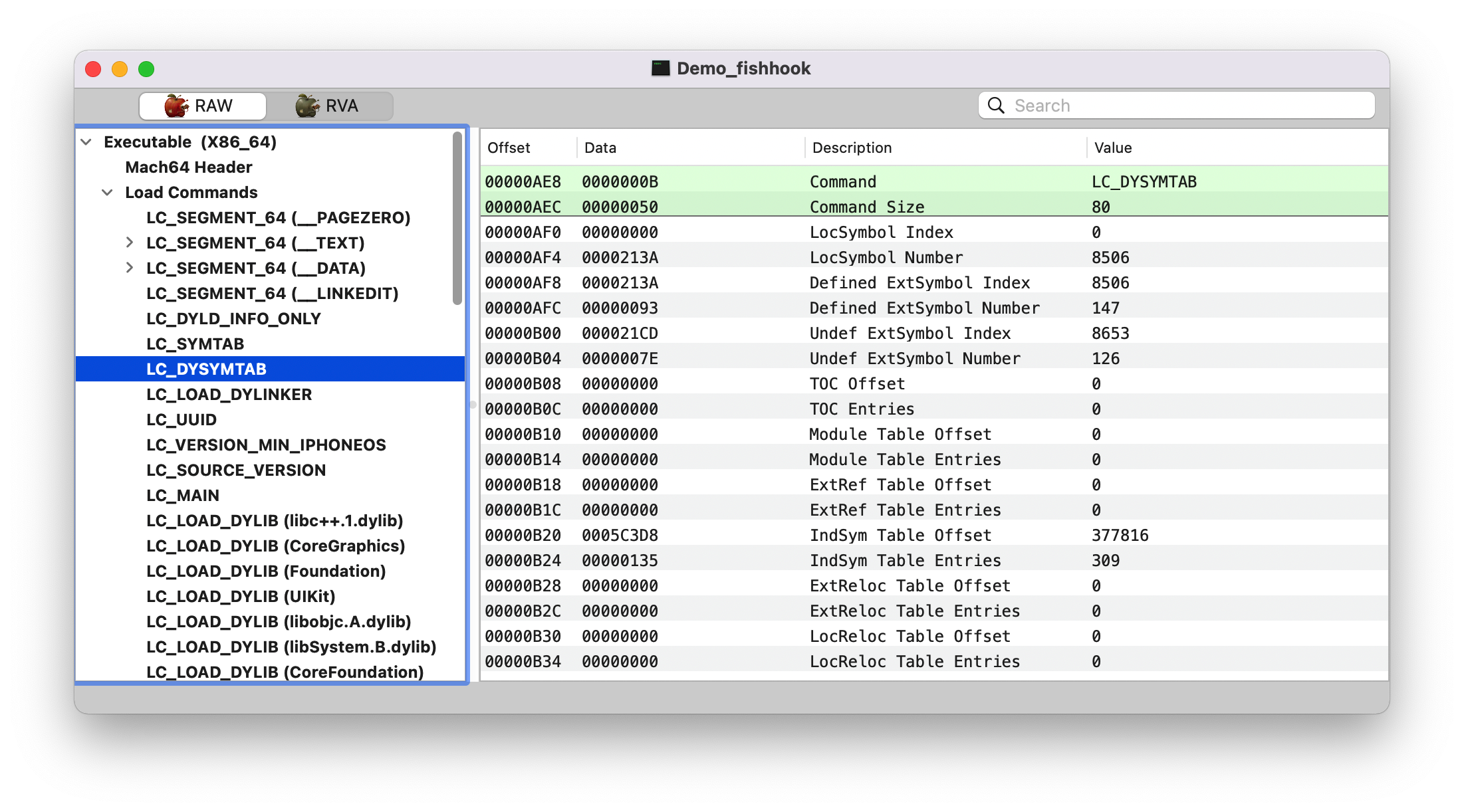
rebind_symbols_for_image 核心方法。
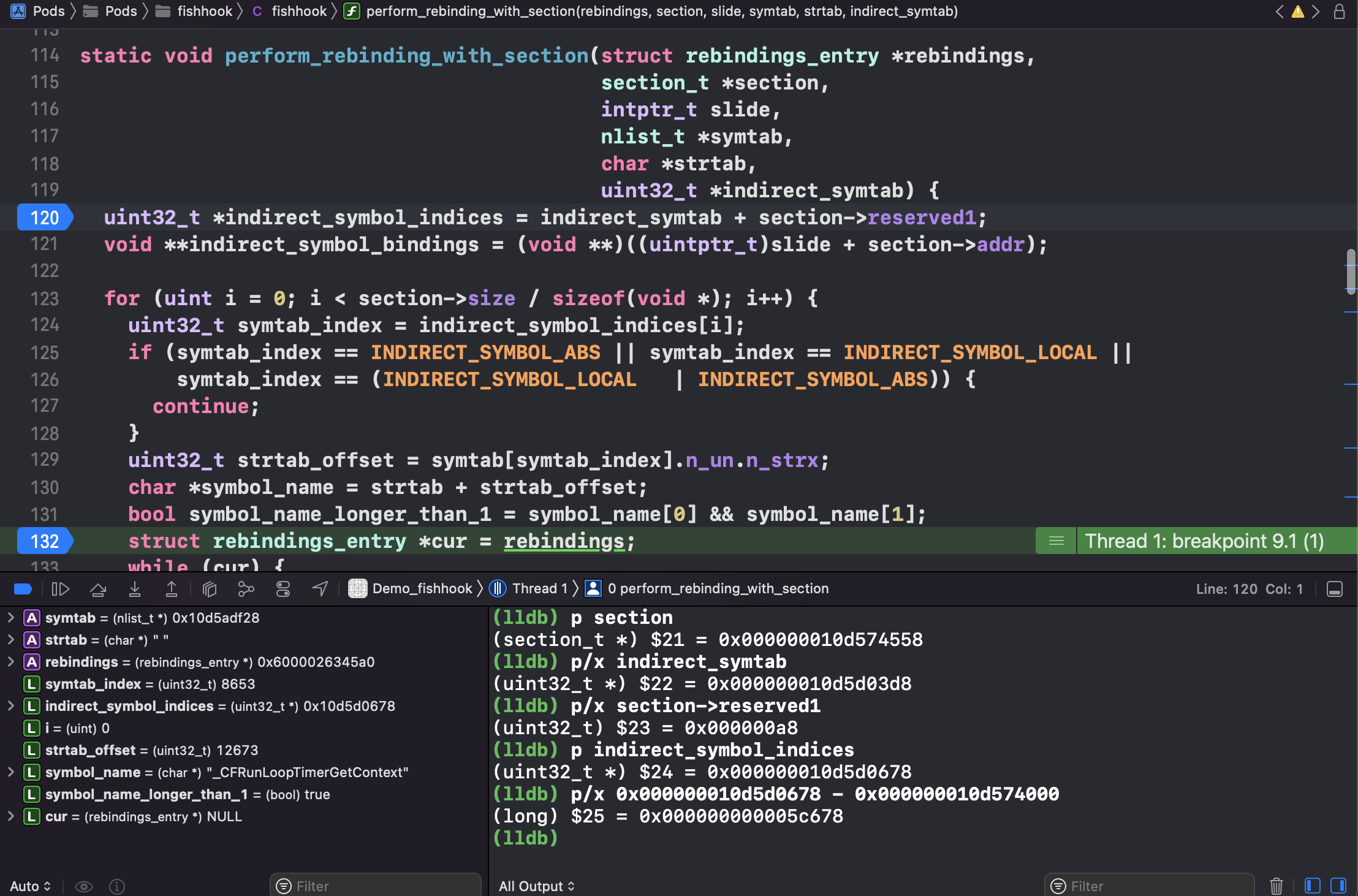
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 static void rebind_symbols_for_image(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings, const struct mach_header *header, intptr_t slide) { Dl_info info; // header 无效 if (dladdr(header, &info) == 0) { return; } // 1. 查找 linkedit_segment symtab_cmd dysymtab_cmd segment_command_t *cur_seg_cmd; segment_command_t *linkedit_segment = NULL; struct symtab_command* symtab_cmd = NULL; struct dysymtab_command* dysymtab_cmd = NULL; // 过掉 Mach-O Header, 到 Load Commands uintptr_t cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t); /* 遍历每个 Load Command header->ncmds: Load Commands 的数量 cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize: 当前 load command 的大小 */ for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) { cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur; // 判断类型是否是 SEG_LINKEDIT LC_SYMTAB LC_DYSYMTAB if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) { if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_LINKEDIT) == 0) { linkedit_segment = cur_seg_cmd; } } else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SYMTAB) { symtab_cmd = (struct symtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd; } else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_DYSYMTAB) { dysymtab_cmd = (struct dysymtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd; } } // 没找到,则 return if (!symtab_cmd || !dysymtab_cmd || !linkedit_segment || !dysymtab_cmd->nindirectsyms) { return; } // Find base symbol/string table addresses /* 2. 获取相关地址值 slide: ASLR 值 vmaddr: 虚拟地址值,fileoff: 文件偏移量,两者相减即可得 VM Size. linkedit_base 就是在虚拟内存加载的基地址(image list 下 image 的值/header) */ uintptr_t linkedit_base = (uintptr_t)slide + linkedit_segment->vmaddr - linkedit_segment->fileoff; nlist_t *symtab = (nlist_t *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->symoff); char *strtab = (char *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->stroff); // Get indirect symbol table (array of uint32_t indices into symbol table) uint32_t *indirect_symtab = (uint32_t *)(linkedit_base + dysymtab_cmd->indirectsymoff); // 3. 查找 section // 游标重置 cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t); for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) { cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur; if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) { if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA) != 0 && strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA_CONST) != 0) { continue; } // __DATA segment load command 后面跟 n 个 sections for (uint j = 0; j < cur_seg_cmd->nsects; j++) { section_t *sect = (section_t *)(cur + sizeof(segment_command_t)) + j; if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) { perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab); } if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) { perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab); } } } } }
查找 linkedit_segment symtab_cmd dysymtab_cmd 这没什么说的,就是常规的查找操作。
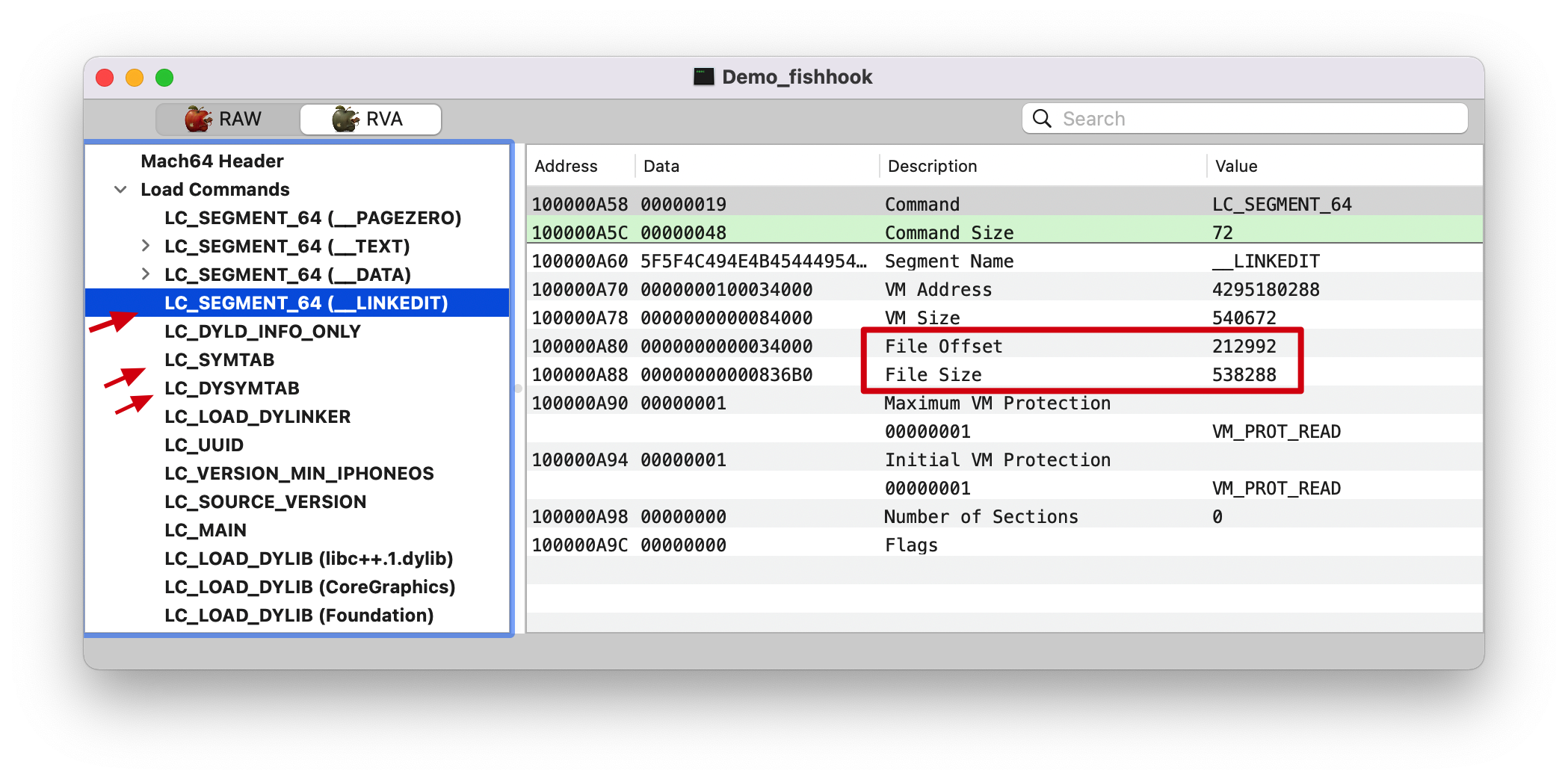
Load Commands 见下面 __LINKEDIT 截图左侧的三个箭头。
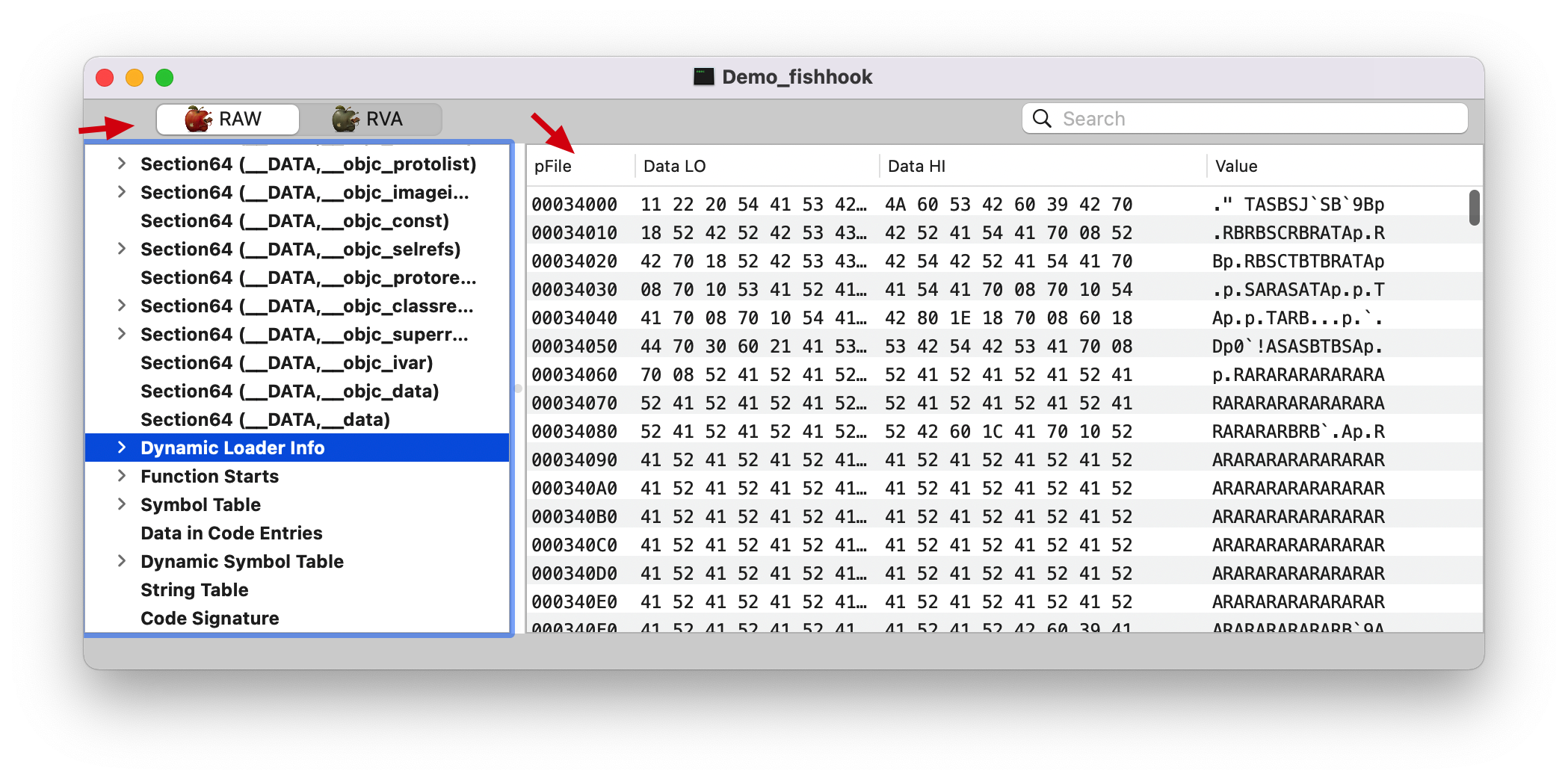
__LINKEDIT __DATA Section 后面的都是 __LINKEDIT Segment,如下图。Note: 这里切换成 RAW 了。
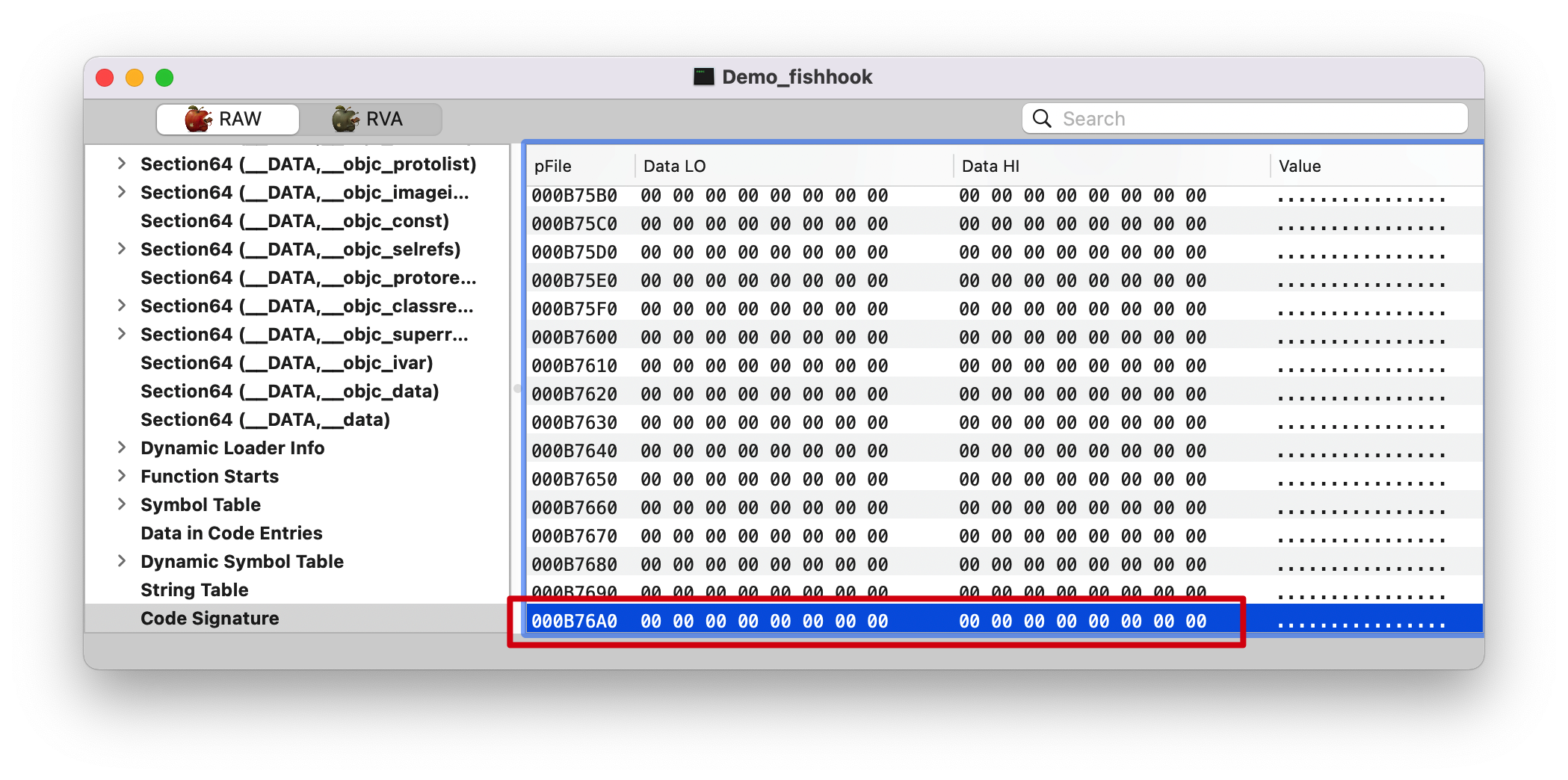
1 2 3 4 (lldb) p/x 0x34000 + 0x836B0 // (int) $5 = 0x000b76b0 (lldb) p/x 0xB76A0 + 0x10 // 16: 0x10 (int) $6 = 0x000b76b0
最后一个 Section 的 index 是 0xB76A0, 占 16Bytes, 也就是 0x000b76b0,没毛病。
LC_SYSTAB
LC_DYSYSTAB
获取相关地址值
从上可知
linkedit_base = header, 就是虚拟内存中加载的基地址
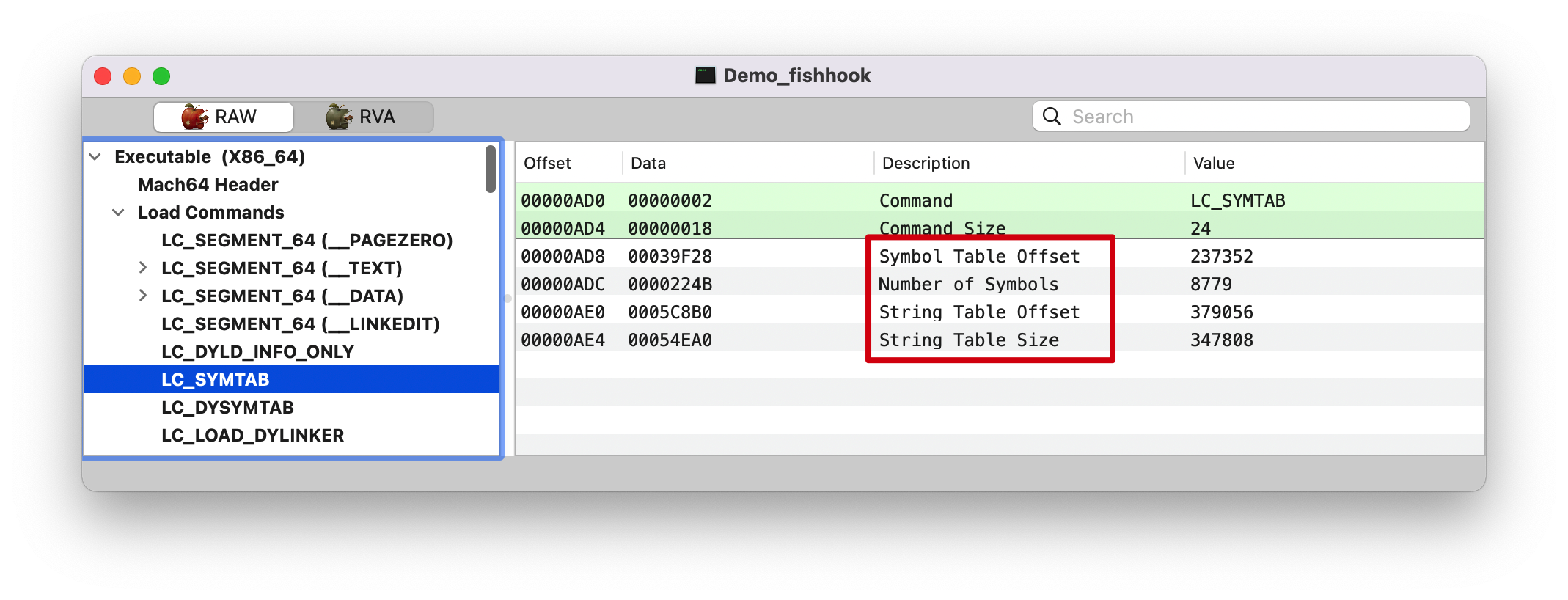
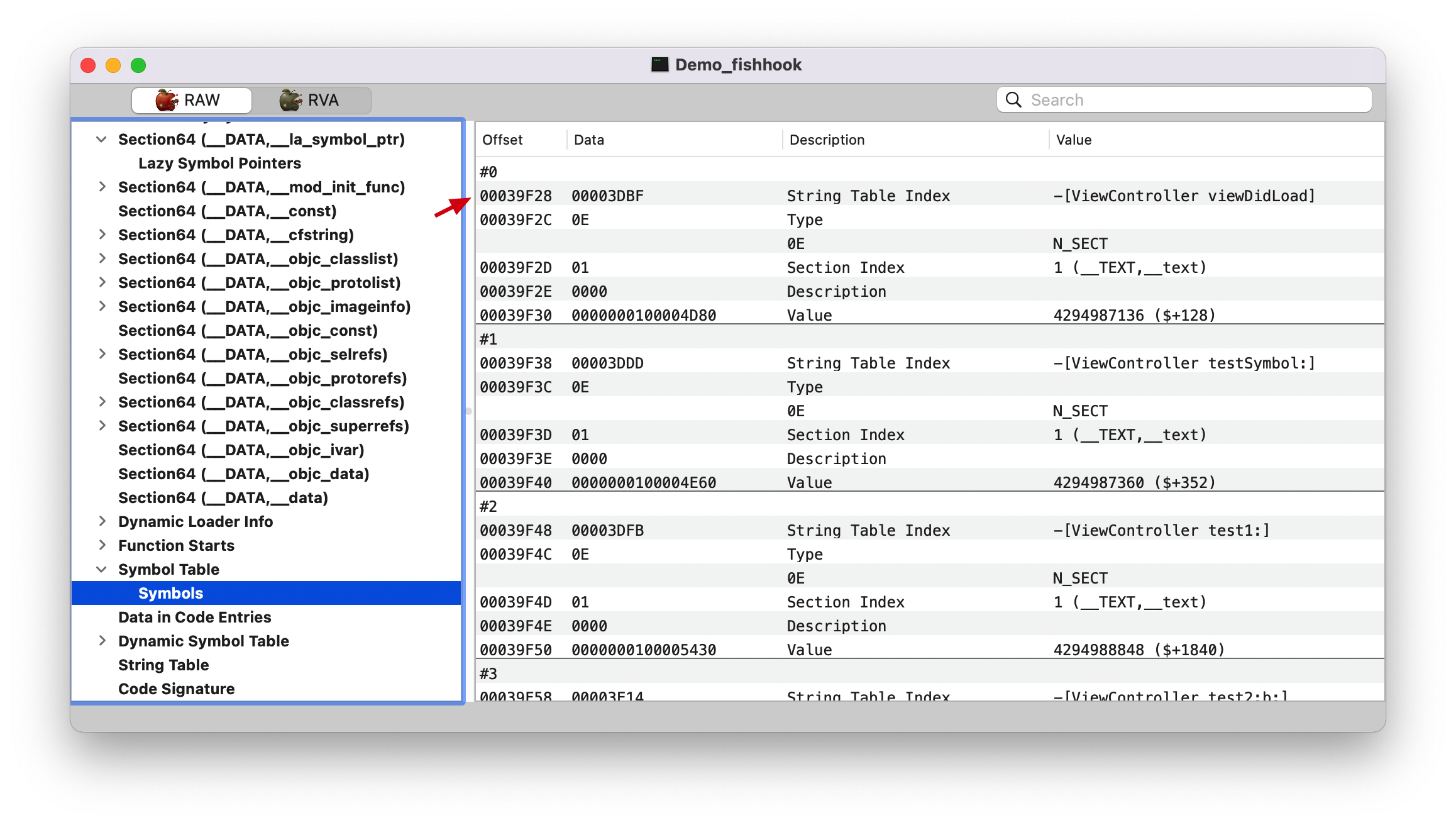
symtab, 看上面的 LC_SYSTAB 截图,Symbol Table Offset (symtab_cmd->symoff): 00039f28
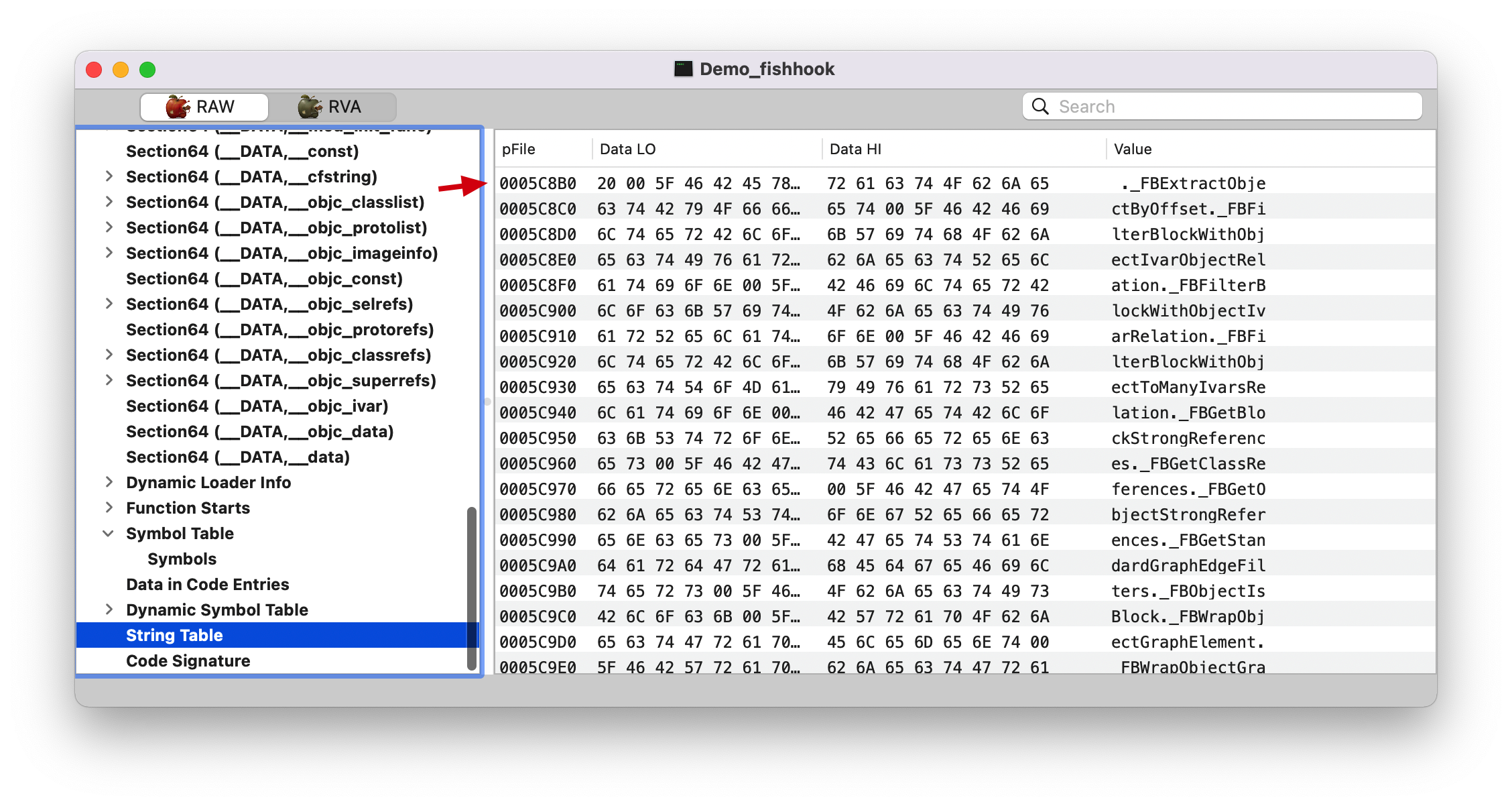
strtab, 看上面的 LC_SYSTAB 截图,String Table Offset (symtab_cmd->stroff): 0005C8B0
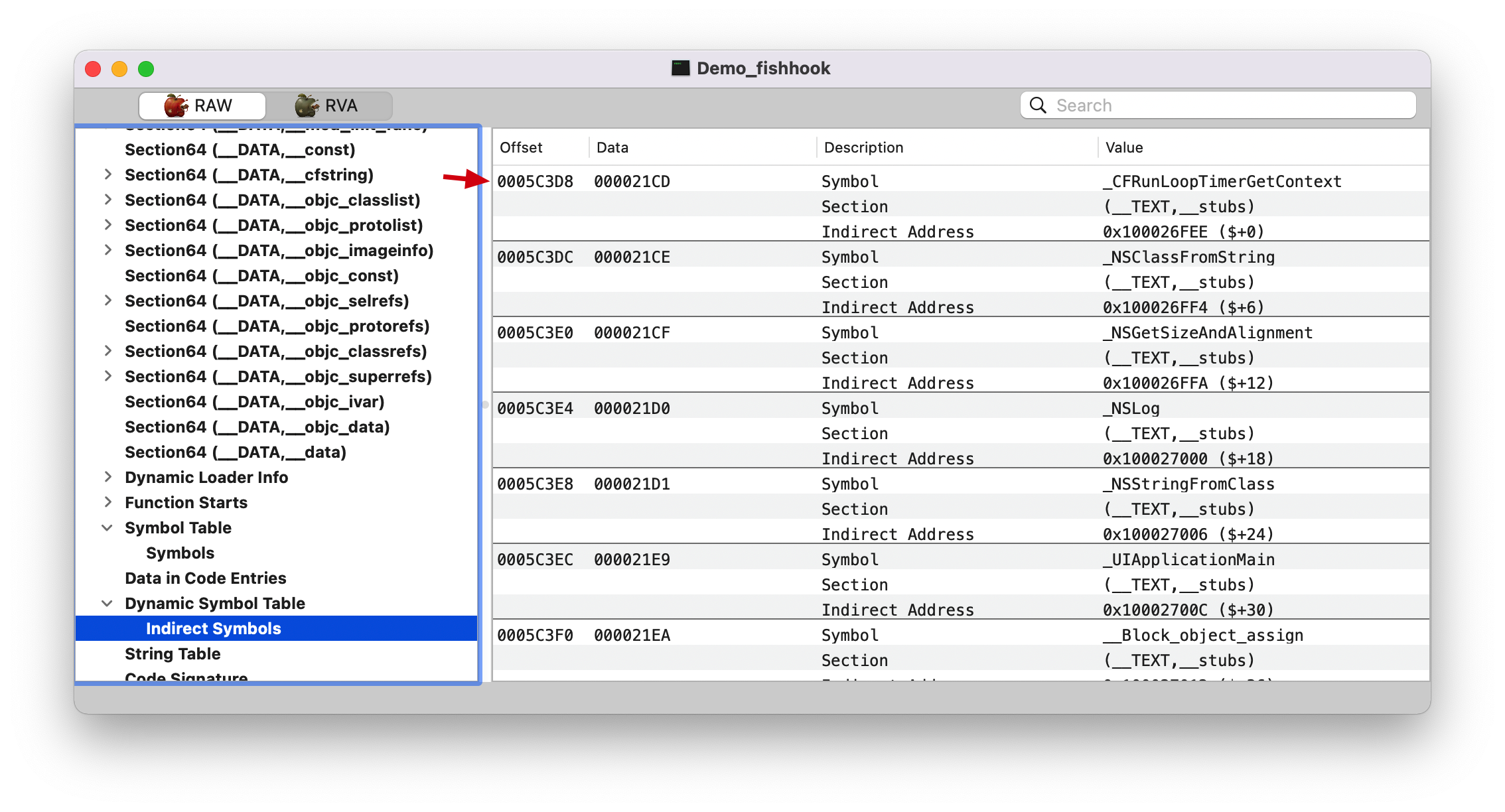
indirect_symtab, 看上面的 LC_DYSYSTAB 截图,IndSym Table Offset: 0005C3D8
查找 section 在 __DATA Segment, 下找到 type 为 S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS/S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTER 的 section。
重新绑定的逻辑,这里以 __la_symbol_ptr Section 为例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 static void perform_rebinding_with_section(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings, section_t *section, intptr_t slide, nlist_t *symtab, char *strtab, uint32_t *indirect_symtab) { // 该 section(__la_symbol_ptr) 在 indirect_symtab 的起始下标, 指向 indirect_symtab uint32_t *indirect_symbol_indices = indirect_symtab + section->reserved1; // 指向具体地址,Section64(__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr) void **indirect_symbol_bindings = (void **)((uintptr_t)slide + section->addr); /* 指针格式 sizeof(void *) = 8, section->size = 1128, 在 MachOView Section64 Header(__la_symbol_ptr), size 也是 1128 所以共 1128/8 = 141 个符号,具体值在 Section64(__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr) */ for (uint i = 0; i < section->size / sizeof(void *); i++) { uint32_t symtab_index = indirect_symbol_indices[i]; // 无效的符号 if (symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS || symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL || symtab_index == (INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL | INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS)) { continue; } // 在字符串表的下标 uint32_t strtab_offset = symtab[symtab_index].n_un.n_strx; // 获取字符串名 char *symbol_name = strtab + strtab_offset; bool symbol_name_longer_than_1 = symbol_name[0] && symbol_name[1]; struct rebindings_entry *cur = rebindings; while (cur) { for (uint j = 0; j < cur->rebindings_nel; j++) { // &symbol_name[1] 去掉函数修饰时前面的 `_`, eg: _NSLog if (symbol_name_longer_than_1 && strcmp(&symbol_name[1], cur->rebindings[j].name) == 0) { kern_return_t err; if (cur->rebindings[j].replaced != NULL && indirect_symbol_bindings[i] != cur->rebindings[j].replacement) // 替换前的原函数地址 *(cur->rebindings[j].replaced) = indirect_symbol_bindings[i]; /** * 1. Moved the vm protection modifying codes to here to reduce the * changing scope. * 2. Adding VM_PROT_WRITE mode unconditionally because vm_region * API on some iOS/Mac reports mismatch vm protection attributes. * -- Lianfu Hao Jun 16th, 2021 **/ err = vm_protect (mach_task_self (), (uintptr_t)indirect_symbol_bindings, section->size, 0, VM_PROT_READ | VM_PROT_WRITE | VM_PROT_COPY); if (err == KERN_SUCCESS) { /** * Once we failed to change the vm protection, we * MUST NOT continue the following write actions! * iOS 15 has corrected the const segments prot. * -- Lionfore Hao Jun 11th, 2021 **/ // 修改函数指向的地方 indirect_symbol_bindings[i] = cur->rebindings[j].replacement; } goto symbol_loop; } } cur = cur->next; } symbol_loop:; } }
SECTION_TYPE 该 header(0x000000010d574000) 会过掉三个 section
0x000000010d5744b8: __nl_symbol_ptr
0x000000010d574508: __got
0x000000010d574558: __la_symbol_ptr
Note: 这里纠正了我之前的一个问题,以为只会处理 __nl_symbol_ptr 和 __la_symbol_ptr 这两个 section 的值,其实不是的,代码里面是判断的类型,而不是根据 Section 名字来的。
1 if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS)
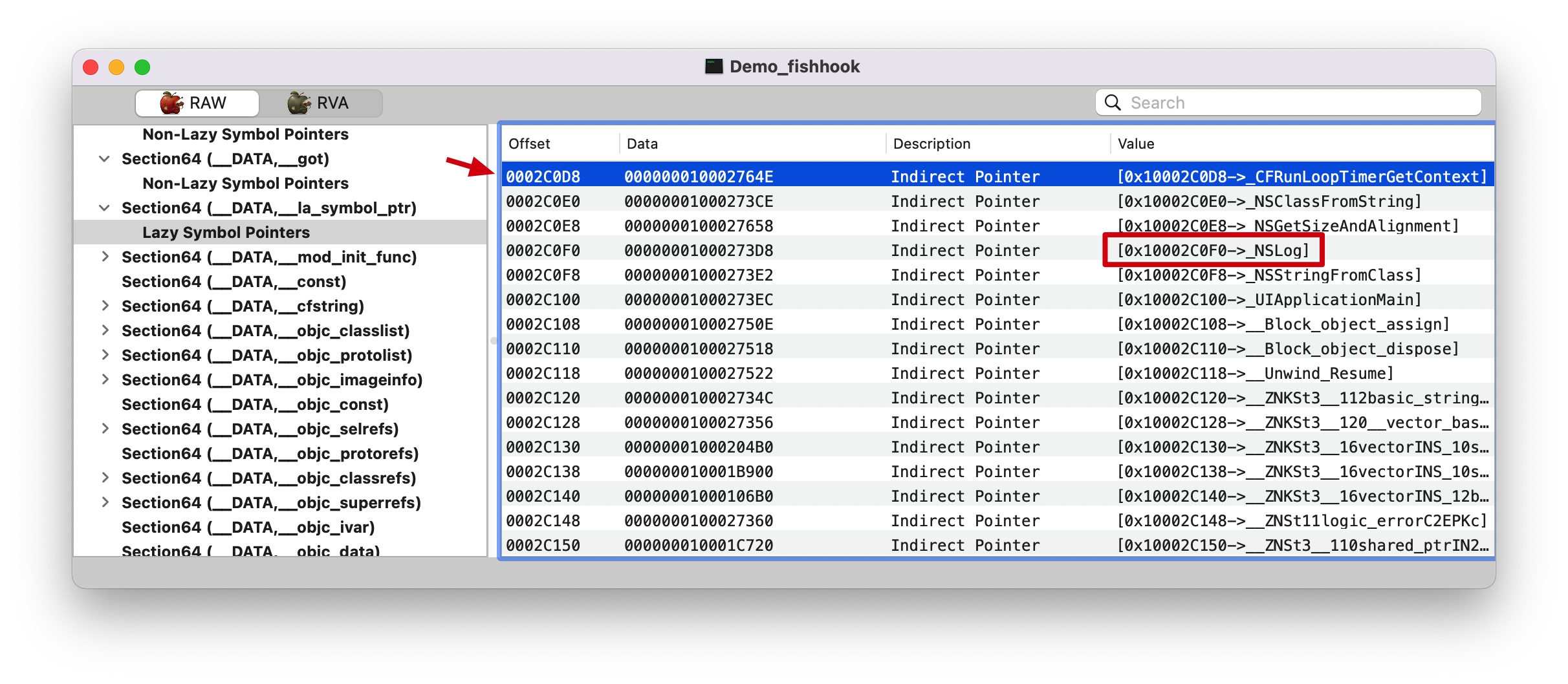
indirect_symtab 只处理 __la_symbol_ptr section.
0xa8=168, 还记得前面的截图Dynamic Symbol Table 开始,第 168 个符号的 Offset 为 0x000000000005c678。
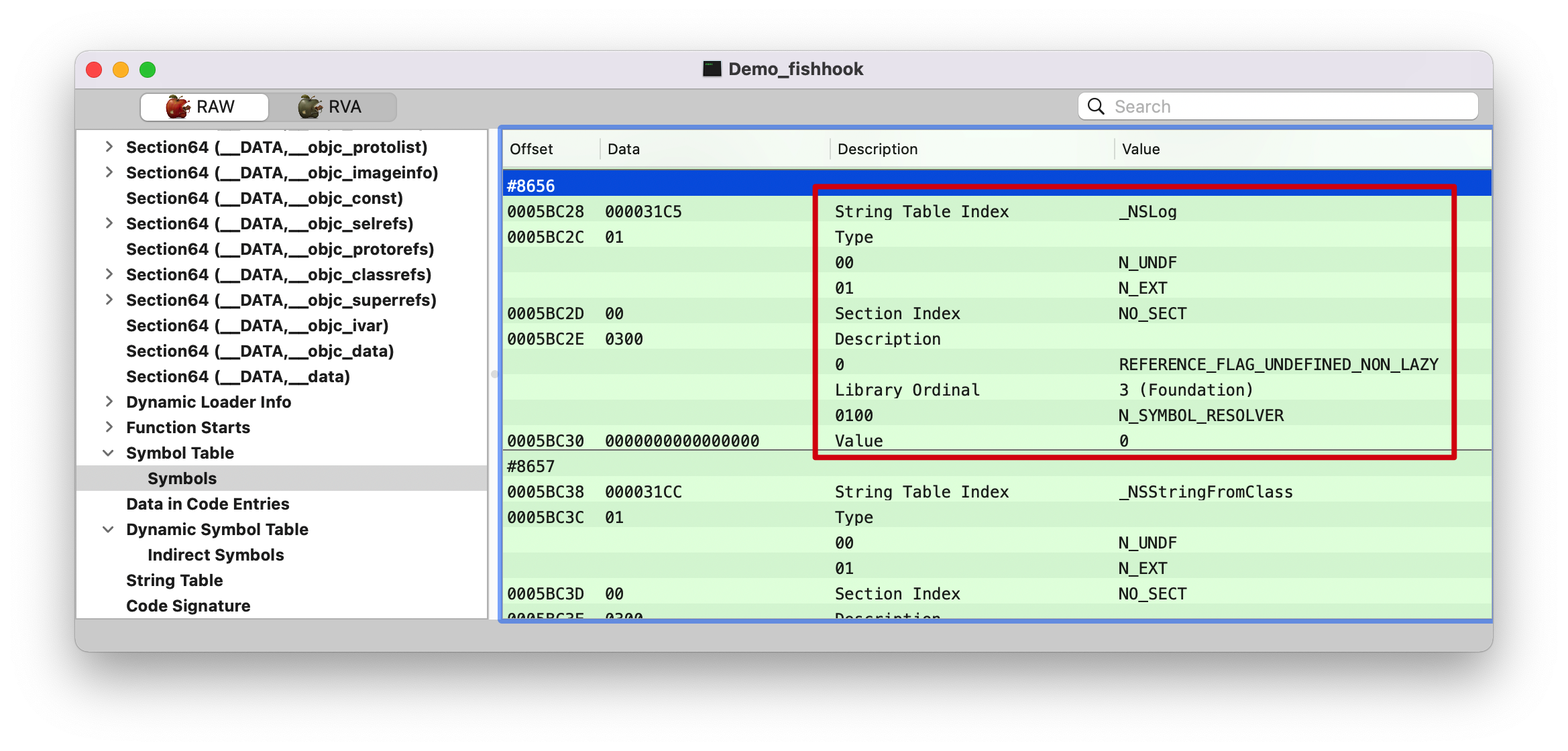
symtab 1 2 (lldb) po symtab_index 8656
在符号表里面找第 8656 个符号。NSLog 来跟踪的。
strtab 1 2 (lldb) p/x 0x0005C8B0 + 0x000031C5 0x5FA75
0005C8B0 是前面 strtab 的起始地址。
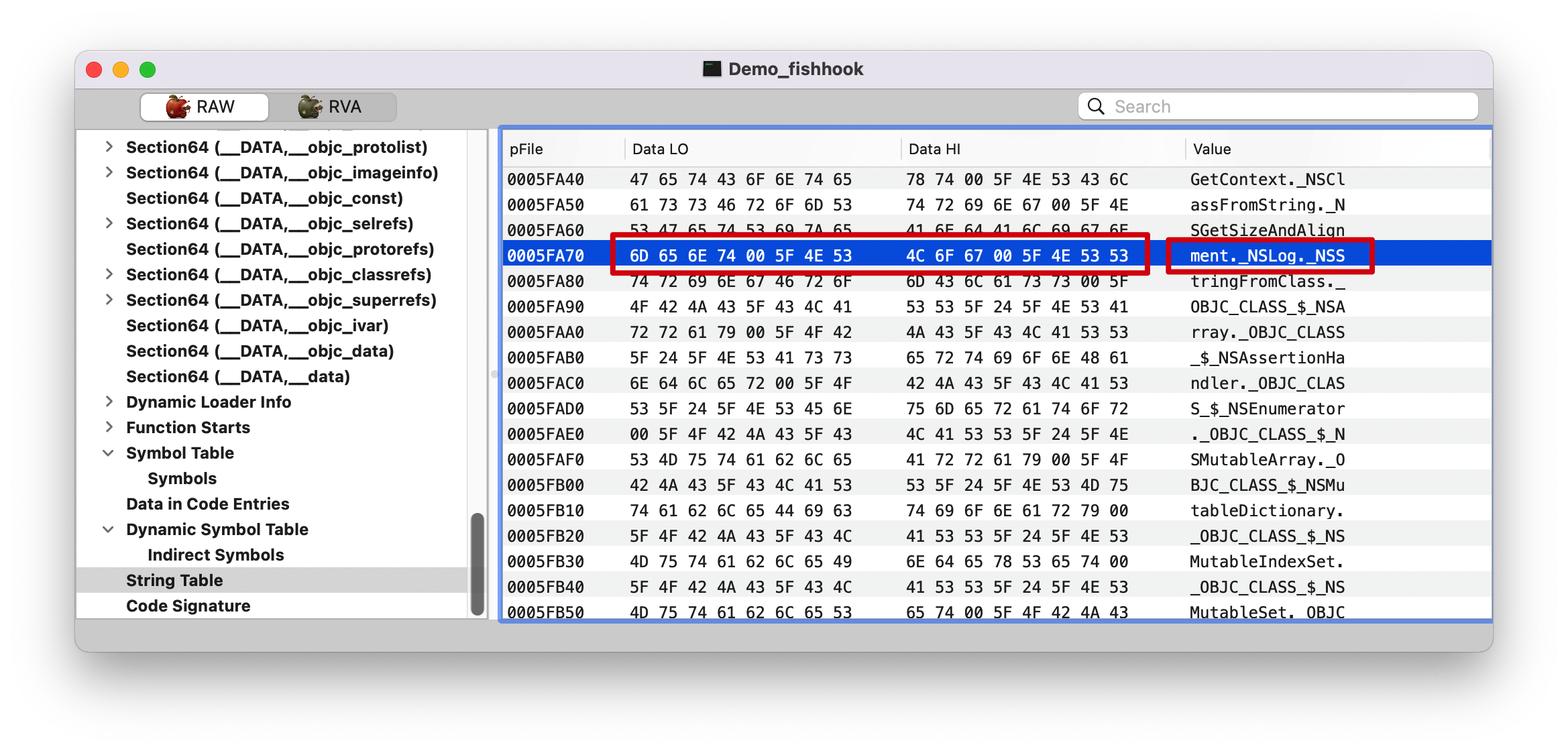
asciitable 。
6D: m
0(00): .
5F: _
4E: N
代码具体地址 1 2 // 指向具体地址,Section64(__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr) void **indirect_symbol_bindings = (void **)((uintptr_t)slide + section->addr);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 (lldb) p/x slide (intptr_t) $52 = 0x000000000d574000 (lldb) p/x section->addr (uint64_t) $53 = 0x000000010002c0d8 (lldb) p indirect_symbol_bindings (void **) $54 = 0x000000010d5a00d8 (lldb) p/x 0x000000010d5a00d8 - 0x000000010d574000 (long) $55 = 0x000000000002c0d8
1 2 3 4 (lldb) p 0x2c540 - 0x2c0d8 (int) $60 = 1128 (lldb) p 1128/8 (int) $61 = 141
0x2c540 是 __DATA,__mod_init_func 的地址。
替换函数地址 1 2 3 4 (lldb) p &indirect_symbol_bindings[i] (void **) $62 = 0x000000010d5a00f0 (lldb) p/x 0x000000010d5a00f0 - 0x000000010d574000 (long) $63 = 0x000000000002c0f0
就是上面截图 NSLog 符号在 Section64(__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr) 的值,因为 indirect_symbol_bindings 是二维指针数组,所以,这里需要进行取地址操作(&),所以这里替换 Section64(__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr)里面的具体地址值。
总结
通过注册系统回调 _dyld_register_func_for_add_image 获取每个 image 的虚拟内存起始地址和 ASLR 偏移
根据 image 的起始地址,加上 Header 的大小(Header 固定大小为 0x20),得出 SEG_LINKEDIT/LC_SYMTAB/LC_DYSYMTAB 这3个 Load Commands 的起始地址
遍历 Load Commands,拿到 __DATA segment 里面类型为 S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS/S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS 的 section (包括 __DATA,__nl_symbol_ptr/__got/__la_symbol_ptr 三个) 的各项信息,包括段的位置,段的大小,段在 Dynamic Symbol Table 的起始索引 reserved1(也就是 MachOView 中的 Indirect Sym Index)
在 Dynamic Symbol Table 遍历相关 Section(eg: Section64(__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr)) 的每个符号,然后找到符号在 LC_SYMTAB 的地址,从而得知该符号的名字
拿到该名字跟需要替换的符号做对比,如果对得上的话,进行替换,修改该 Section 下对应符号的指针指向
扩展 lldb - image 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 (lldb) image help Commands for accessing information for one or more target modules. Syntax: target modules <sub-command> ... The following subcommands are supported: add -- Add a new module to the current target's modules. dump -- Commands for dumping information about one or more target modules. list -- List current executable and dependent shared library images. load -- Set the load addresses for one or more sections in a target module. lookup -- Look up information within executable and dependent shared library images. search-paths -- Commands for managing module search paths for a target. show-unwind -- Show synthesized unwind instructions for a function. (lldb) help image lookup Look up information within executable and dependent shared library images. Syntax: target modules lookup <cmd-options> [<filename> [<filename> [...]]] Command Options Usage: target modules lookup [-Av] -a <address-expression> [-o <offset>] [<filename> [<filename> [...]]] target modules lookup [-Arv] -s <symbol> [<filename> [<filename> [...]]] target modules lookup [-Aiv] -f <filename> [-l <linenum>] [<filename> [<filename> [...]]] target modules lookup [-Airv] -F <function-name> [<filename> [<filename> [...]]] target modules lookup [-Airv] -n <function-or-symbol> [<filename> [<filename> [...]]] target modules lookup [-Av] -t <name> [<filename> [<filename> [...]]] -A ( --all ) Print all matches, not just the best match, if a best match is available. -F <function-name> ( --function <function-name> ) Lookup a function by name in the debug symbols in one or more target modules. -a <address-expression> ( --address <address-expression> ) Lookup an address in one or more target modules. -f <filename> ( --file <filename> ) Lookup a file by fullpath or basename in one or more target modules. -i ( --no-inlines ) Ignore inline entries (must be used in conjunction with --file or --function). -l <linenum> ( --line <linenum> ) Lookup a line number in a file (must be used in conjunction with --file). -n <function-or-symbol> ( --name <function-or-symbol> ) Lookup a function or symbol by name in one or more target modules. -o <offset> ( --offset <offset> ) When looking up an address subtract <offset> from any addresses before doing the lookup. -r ( --regex ) The <name> argument for name lookups are regular expressions. -s <symbol> ( --symbol <symbol> ) Lookup a symbol by name in the symbol tables in one or more target modules. -t <name> ( --type <name> ) Lookup a type by name in the debug symbols in one or more target modules. -v ( --verbose ) Enable verbose lookup information. This command takes options and free-form arguments. If your arguments resemble option specifiers (i.e., they start with a - or --), you must use ' -- ' between the end of the command options and the beginning of the arguments. 'image' is an abbreviation for 'target modules'
比如
image list: 输出当前进程所依赖的共享库
image list -o -f: 上个命令简洁版,输出相关库的 ASLR 地址(o: offset)
image lookup -n xxx: 输出 xxx 符号的相关信息
image lookup -t xxx: 输出 xxx 符号的类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 (lldb) image lookup -n NSLog 1 match found in /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Library/Developer/CoreSimulator/Profiles/Runtimes/iOS.simruntime/Contents/Resources/RuntimeRoot/System/Library/Frameworks/Foundation.framework/Foundation: Address: Foundation[0x00000000000f7762] (Foundation.__TEXT.__text + 1006242) Summary: Foundation`NSLog (lldb) image lookup -t FBBlockStrongRelationDetector 0 match found in /Users/joakim/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/Demo_fishhook-ebwkhxbcogafxbclcdeifrppsgdu/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/Demo_fishhook.app/Demo_fishhook: id = {0x00071c41}, name = "FBBlockStrongRelationDetector", byte-size = 176, decl = FBBlockStrongRelationDetector.h:23, compiler_type = "@interface FBBlockStrongRelationDetector : NSObject{ void * forwarding; int flags; int size; void (*)(_block_byref_block *, _block_byref_block *) byref_keep; void (*)(_block_byref_block *) byref_dispose; void *[16] captured; BOOL _strong; } @property(nonatomic, assign, readwrite, getter = isStrong, setter = setStrong:) BOOL strong; @end"
antifishhook 从前面可知 fishhook 的原理就是修改相关 Section __DATA,__nl_symbol_ptr/__got/__la_symbol_ptr 下对应符号的指向。NSLog 的时候走 __stub_helper 的逻辑。AntiHook ,代码是用 Swift 实现的,值得一看。
参考链接